GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science chapter 11 – Human Eye and Colourful World
Back Exercise
Question 1.
Choose the correct option :
Human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near sightedness
(d) far sightedness.
Answer:
(b) accommodation.
Question 2.
Human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea
(b) iris
(c) pupil
(d) retina.
Answer:
(d) retina.
Question 3.
The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about (CBSE 2012, Bihar Board 2012)
(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 50 cm. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(c) 25 cm.
Question 4.
The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of
(a) pupil
(b) retina
(c) ciliary muscles
(d) iris. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(c) ciliary muscles.
Question 5.
A person needs a lens of power – 5.5 diopters for correcting distant vision. For correcting his near vision, he needs a lens of power +1.5 diopter. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting
(i) distant vision and
(ii) near vision ?
Answer:

Question 6.
The far point of a myopic person is 150 cm in front the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem ?
Answer:

The lens is concave lens.
Question 7.
Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect ? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
(CBSE 2011)
Answer:
For diagram,
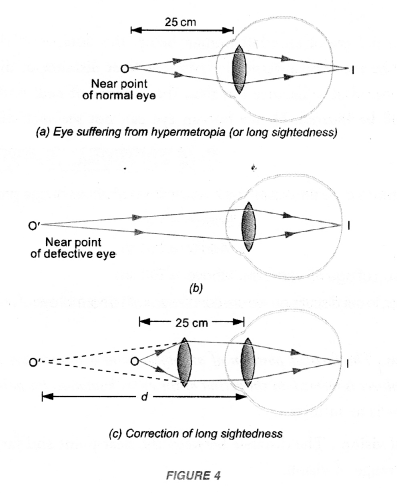
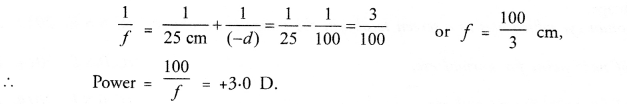
Question 8.
Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
The nearest position of an object from a normal human eye so that its sharp image is formed on retina is 25 cm. If the object is placed at a distance less than 25 cm, then the blurred image of the object is formed on retina as the focal length of eye lens cannot be decreased below a certain limit. Hence, eye cannot see it clearly.
Question 9.
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye ?
[CBSE (Delhi) 2008, 2011]
Answer:
The image distance remains the same in the eye because the eye has the ability to change the focal length of its lens to make the image always on the retina when the object distance increases from the eye.
Question 10.
Why do stars twinkle ? (CBSE 2011, 2012, 2015, 2016)
Answer:
The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of
starlight. The starlight, on entering the earth’s atmosphere,
undergoes refraction continuously before it reaches the earth.
The atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually
changing refractive index. This apparent
position of the star is not stationary, but keeps on changing
slightly, since the physical conditions of the earth’s
atmosphere are not stationary. Since the stars are very distant, they
approximate point-sized sources of light. As the path of rays
of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the
apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of
starlight entering the eye flickers – the star sometimes appears brighter,
and at some other time, fainter, which is the twinkling effect.
Question 11.
Explain why the planets do not twinkle. (CBSE 2011, 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Planets do not twinkle:
Planets are very close to the earth as compared to the stars. The planets act as extended sources of light. So the intensity of light we receive from the planets is very large. Therefore, variation in the amount of light entering our eye from planets becomes zero, thereby
nullifying the twinkling effect.
Question 12.
Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning ? (CBSE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
During sunrise, the light rays coming from the Sun have to travel a greater distance in the earth's atmosphere before reaching our eyes. In this journey, the shorter wavelengths of lights are scattered out and only longer wavelengths are able to reach our eyes. Since blue colour has a shorter wavelength and red colour has a longer wavelength, the red colour is able to reach our eyes after the atmospheric scattering of light. Therefore, the Sun appears reddish early in the morning.
Question 13.
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut ?
Answer:
The blue colour of sky is due to the scattering of sunlight. The scattering of sunlight in the atmosphere is due to the presence of atoms and molecules of gases, droplets and dust particles. When the astronaut is in space, then there is no atmosphere (or atoms and molecules of gases, droplets and dust particles) around him. Therefore, sunlight does not scatter and hence sky appears dark.
In-Text Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye ?
(CBSE Sample Paper 2010, 2012, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017)
Answer:
The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length to see nearby and distant objects clearly.
Question 2.
A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision ?
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision ? (CBSE 2011, 2012, 2014)
Answer:
The farthest position of an object from the human eye so that its sharp image is formed on the retina is at infinite distance from the eye.
The nearest position of an object from a human eye so that its sharp image is formed on the retina is at 25 cm from the eye.
Question 4.
A student has difficulty in reading the black board while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from ? How can it be corrected ? (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The student is suffering from short-sightedness or myopia. Myopia can be corrected by the use of concave or diverging lens of an appropriate power.