GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography chapter 2 – Inside Our Earth
Back Exercise
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
- What are the three layers of the earth?
- What is a rock?
- Name three types of rocks.
- How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
- What do you mean by a rock cycle?
- What are the uses of rocks?
- What are metamorphic rocks?
Answer.
1. Crust, mantle, and core are the three layers of the earth.
2. A rock is a natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust.
Rocks can be of a different colour, size, and texture.
3. The three types of rocks are:
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks.
4. When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way on the crust are extrusive rocks. Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are actually intrusive rocks.
5. The change of one type of rock into another under certain conditions in a cyclic manner is called a rock cycle.
6. Uses of rocks:
(i) Hard rocks are used in construction of buildings and roads.
(ii) Some rocks are shiny and precious therefore used for making jewellery.
(iii) Rocks are made up of different minerals and are very important to humankind.
(iv) Some are used as fuels. For example, coal, natural gas and petroleum.
(v) Soft rocks are used for making talcum powder, chalks etc.
7. The type of rocks formed when igneous and sedimentary rocks undergo heat and pressure are called metamorphic rocks.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) The rock which is made up of molten magma is
(a) Igneous
(b) Sedimentary
(c) Metamorphic
Answer.
(a) Igneous
(ii) The innermost layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Core
(c) Mantle
Answer.
(b) Core
(iii) Gold, petroleum, and coal are examples of
(a) Rocks
(b) Minerals
(c) Fossils
Answer.
(b) Minerals
(iv) Rocks which contain fossils are
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks
Answer.
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(v) The thinnest layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Mantle
(c) Core
Answer.
(a) Crust.
Question 3.
Match the following.
(i) Core (a) Earth’s surface
(ii) Mineral (b) Used for roads and buildings
(iii) Rocks (c) Made of silicon and alumina
(iv) Clay (d) Has the definite chemical composition
(v) Sial (e) Innermost layer
(f) Changes into slate
(g) Process of transformation of the rock
Answer.
(i) Core (e) Innermost layer.
(ii) Mineral (d) Has definite chemical composition.
(iii) Rocks (b) Used for roads and buildings.
(iv) Clay (f) Changes into slate
(v) Sial (c) Made of silicon and alumina.
Question 4.
Give reasons.
- We cannot go to the center of the earth.
- Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments.
- Limestone is changed into marble.
Answer.
1. We cannot go to the centre of the earth because the temperature and pressure at the centre of the earth are very high and not just human beings, but even rocks melt at the centre of the Earth.
2. Rocks breakdown into small fragments tinders various conditions. These fragments, called sediments, are transported by wind and water. Layers of sediments are formed when loose sediments are compressed and hardened. These layers of sediments thus form sedimentary rocks.
3. Igneous and sedimentary rocks change their form under great pressure and temperature conditions to form metamorphic rocks. The same thing happens with limestone, which under the effect of heat and pressure changes into marble, which is an example of metamorphic rock.
Question 5.
For fun.
(i) What are the minerals most commonly used in the following objects?
(ii) Identify some more objects made up of different minerals.
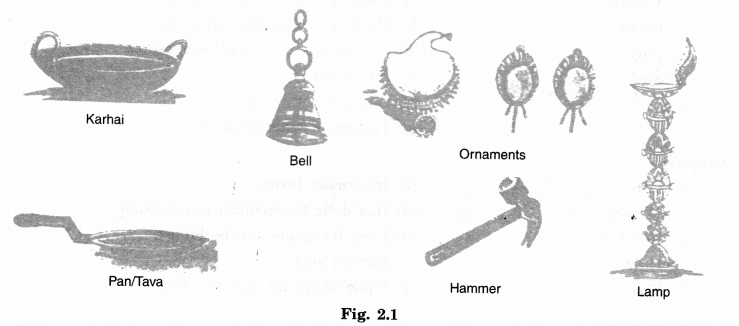
Answer.
- Karhai – Iron
Bell – Brass
Ornaments – Gold
Pan/Tava – Iron
Hammer – Iron
Lamp – Brass - Identification
Other more things, utensils (steel, brass, copper, aluminium) Furniture (iron), windows (iron, glass, aluminium).
In-Text Questions
Question 1.
Collect pictures of some monuments and find out which are rocks used to build them. Two pictures have been collected for you. (NCERT Page 9)
Answer.
- The Taj Mahal is made of white marble.
- The Red Fort is made of red sandstone.
Question 2.
What are the minerals found in your state? (NCERT Page 10)
Answer.
- No minerals are found in our state, Delhi, (National Capital Territory of Delhi).
- Only Badarpur and stone are extracted from Bhati mines.
Jharkhand: Following minerals are mainly found in my state:
- Coal
- Iron Ore
- Aluminium (Bauxite)
- Uranium
- Mica