GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Geography chapter 4 – Agriculture
Back Exercise
Multiple choice questions(i) Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
(a) Shifting Agriculture
(b) Plantation Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive Agriculture
► (b) Plantation Agriculture
(ii) Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice
(b) Gram
(c) Millets
(d) Cotton
► (b) Gram
(iii) Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses
(b) Jawar
(c) Millets
(d) Sesamum
► (a) Pulses
2. Answer the following questions in 30 words.
(i) Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
(ii) Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
(iii) Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
(iv) The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Answer
(i) Tea is an important beverage crop. This plant grows well in tropical or sub tropical climates, and deep and fertile well-drained soil which is rich in humus and organic matter.
(ii) Rice is a staple food crop of India. It grows in the plains of north and north-east India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions.
(iii) The various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government for the benefit of farmers are:
→ Crop insurance against drought, flood, fire etc.
→ Minimum Support Price policy.
→ Subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilisers.
→ Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme.
(iv) A declining area of land under cultivation coupled with increasing population have many consequesnces. These are:
→ Food shortage for the rising population.
→ Rise in price of food grains.
→ Unemployment and loss of livelihood for farmers.
→ Shortage of supply of raw material for agro-industries.
→ Adverse affect on export trade as agricultural products comprise a major section of international trade.
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
(ii) Describe the impact of globalisation on Indian agriculture.
(iii) Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer
Various initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production are:
→ Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of Zamindari etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after independence.
→ Land Reform was the main focus of our ‘First Five Year Plan’.
→ The Green Revolution was based on the use of package technology and the White Revolution were some of the strategies initiated to improve the lot of Indian agriculture.
→ Minimum Support Price policy, provision for crop insurance, subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilizers, Grameen Banks, Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme are also some of the reforms bought by Indian Government.
(ii) The impact of globalisation on Indian agriculture has been felt since colonial times. Raw cotton and spices were important export items from India. In 1917, Indian farmers revolted in Champaran against being forced to grow indigo in place of foodgrains, in order to supply dye to Britain's flourishing textile industry. Thus, globalisation has had its boons and banes for Indian agriculture.
Post liberalisation, Indian farmers face new challenges in the form of competition from highly subsidised agriculture of developed nations. This prompts the need for making Indian agriculture successful and profitable by improving the conditions of small and marginal farmers, countering the negative effects of Green Revolution, developing and promoting organic farming, and diversifying cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops.
Post liberalisation, Indian farmers face new challenges in the form of competition from highly subsidised agriculture of developed nations. This prompts the need for making Indian agriculture successful and profitable by improving the conditions of small and marginal farmers, countering the negative effects of Green Revolution, developing and promoting organic farming, and diversifying cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops.
(iii) The geographical conditions required for growth of rice are as follows :
→ It is a kharif crop and requires hot and humid climate for cultivation. Temperature above 25°C and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm are favourable for growth of rice.
→ Rich alluvial soils of the floodplains and deltaic areas which are renewed every years are ideal for rice cultivation.
→ Rice requires abundant rainfall or good water supply through irrigation and flooded fields during the earlier part of its growing season in June-July.
→ Plenty of cheap labour as most of the farming involves manual labour.
Project Work
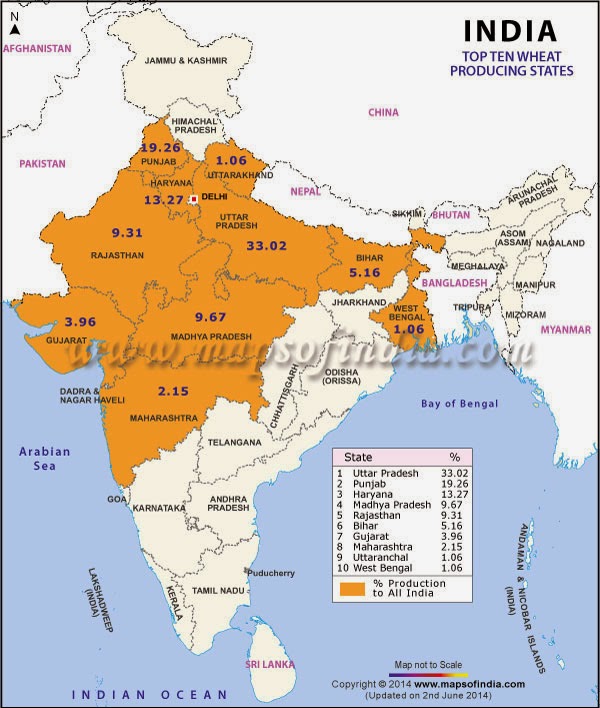
2. On an outline map of India show wheat producing areas.
Answer
3. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
1. The two staple food crops of India.
2. This is the summer cropping season of India.
3. Pulses like arhar, moong, gram, urad contain…
4. It is a coarse grain.
5. The two important beverages in India are…
6. One of the four major fibers grown on black soils.
Answer
1. Rice and Wheat
2. Kharif
3. Protein
4. Jowar
5. Coffee, Tea
6. Cotton