GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography chapter 5 – Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Back Exercise
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:(a) Tundra
(ii) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than:
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) Less than 50 cm
► (a) 100 cm
(iii) In which of the following states is the Simplipal bioreserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal
► (c) Odisha
(iv) Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserve?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Nanda Devi
► (a) Manas
Page No: 52
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Define an ecosystem.
(ii) What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
(b) Climate: Temperature, Humidity, Photoperiod and Precipitation.
Montane animals: Snow Leopard, Spotted dear
3. Distinguish between
(i) Flora and Fauna
(ii) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous forests
Answer
(i)
Flora
|
Fauna
|
| The Plant species of particular region or period are called Flora. | The animal species of particular region or period are called Fauna. |
(ii)
Tropical Evergreen Forests
|
Tropical Deciduous Forests
|
| These are also called Rain Forest | These are also called Monsoon Forest. |
| Since the region is warm and wet throughout the year, there is no definite time for the trees to shed their leaves | The trees shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in dry summer |
| Examples: ebony, mahogany, rubber, rosewood | Examples: teak, bamboo, sandalwood, peepal, neem |
| Common animals found in these forests are elephants and monkeys. | Common animals found in these forests are lions and tigers |
| Present in areas receiving more than 200 cm of rainfall | Present in areas receiving rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm |
4. Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Answer
The different types of vegetation found in India are:
(i) Tropical Evergreen Forests
(ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests
(iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
(iv) Montane Forests
(v) Mangrove Forests
Alpine vegetation is found at places over 3,600 m in height. The trees common to these are silver fir, junipers, pines and birches. The trees get stunted as they reach the snow line. There are shrubs and scrubs that ultimately merge into Alpine grasslands. Tundra vegetation is limited to lichens and mosses.
5. Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Answer
Few species of plants and animals are endangered in India because of:
→ Increase in population.
→ Urbanization and Industrialization.
→ Large scale deforestation.
→ Pollution.
→ Hunting for pleasure and commercial purpose, etc.
6. Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Answer
India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to following reasons:
→ India is a diverse country with different relief features (i.e. mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.) Different types of vegetations are found in these regions and the vegetations support different type of animals.
→ Availability of different types of soil providing base for different type of vegetations.
→ Variation in the climatic conditions (Temperature, humidity, etc.). Climate of India differs from north to south and east to west. Thus, supporting large variety of flora and fauna.
→ India has a monsoon type of climate where rainfall varies from 20 cms to 300 cms distributed through out the year supporting large amount of flora and fauna.
→ Variation in the duration of sunlight at different places due to difference in the latitude and altitude.
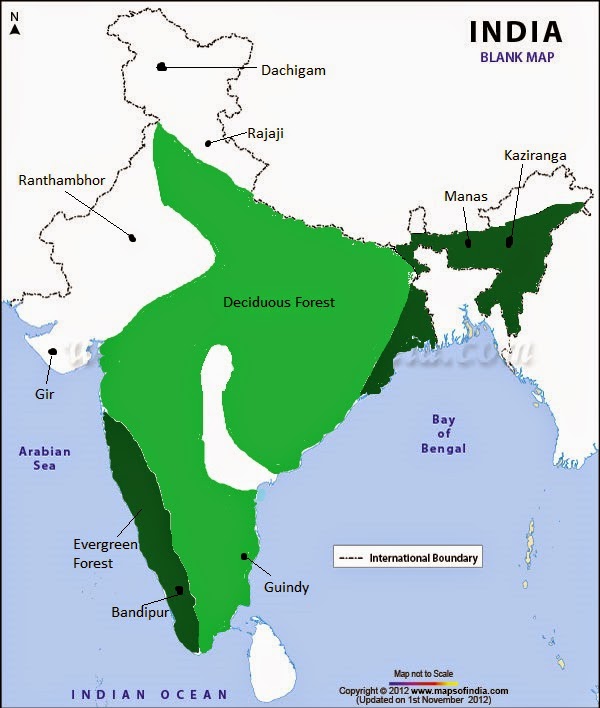
Map Skills
On an outline map of India, label the following.
(i) Areas of Evergreen Forests
(ii) Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
(iii)Two national parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western parts of the Country
Answer
In-Text Questions
Page 43
Question 1. Why are the southern slopes in Himalayan region covered with thick vegetation cover as compared to northern slopes of the same hills?
Answer The growth of vegetation depends upon the amount sunlight and rainfall received. The southern slopes of the Himalaya receive more rain due to the south west monsoon winds which travel west along the southern slops. The northern slopes do not receive any such rainfall. So the southern slopes are covered with thick vegetation as compared to the northern slopes.
Question 2. Why have the western slopes of the Western Ghats covered with thick forests and not the eastern slopes?
Answer It is because the western slope get much heavier rainfall than the eastern slopes. Moisture laden air moves eastwards across, the Western Ghats during the monsoon season.
Question 3. Study the bar graph and answer the following questions
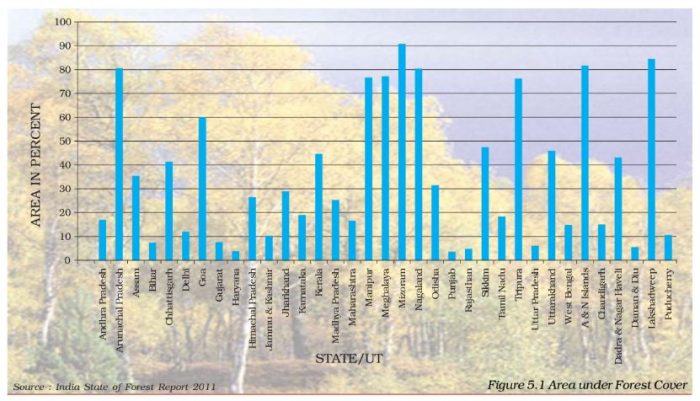
(i) Name the state having maximum area under forest cover.
(ii) Name the union territory having minimum area under forest cover and give the reason why.
Answer
(i) Nagaland
(ii) Lakshadweep is the union territory having minimum forest cover. Since Lakshadweep consists only of coral islands, they have no proper soil for growing of forests except for coconut trees. Since these are commercially viable there is no declared forest in Lakshadweep.
Page 47
Question 1. What will happen if plants and animals disappear from the Earth’s surface? Can human beings survive under such a situation? Why is biodiversity necessary and why should it be conserved?
Answer
(a) If the plants and animals disappear from the Earth’s surface, then the ecological balance will be disturbed. Without plants there will be no oxygen available for breathing after some time and everybody will die.
(b) Biodiversity means biological diversity, 1.e., there are many animal and plant species on our planet spread all over the world. These animal and plant species, including humans, are all interdependent
(c) Each species has its own place and role to play in the environment and help in the maintaining the ecological balance. That’s why it should be conserved.
Page 48
Question 1. Identify some medicinal plants in your area. Which plants are used as medicines by local people to cure diseases?
Answer Some medicinal plants found in our area with diseases they can cure are given below :
(i) Bel Fruit : The ripe fruit cures gastro intestinal problems.
(ii) Iswarmula Root : Its decoction cures constipation.
(iii) Satawari Tuber : It cures gastro intestinal problems.
(iv) Iswarmula Root : Decoction of root is given in constipation and abdominal colic.
(v) Dimiri Leaf and Stem : Fresh juice (50-100 mL) of leaves is given with water for about 10 days to treat gastro intestinal problems.
Page 50
(i) Find out from the above newspaper cuttings the main concern highlighted in the given news items.
Answer The main concern highlighted in the given news items is that wildlife in India is endangered and some species may get extinct soon. The rhinos, tigers, vultures and gulls are being killed by poachers or are dying.
(iii) Find out various steps taken by the Indian Government to protect them.
Answer The Indian Government has taken the following steps to protect the endangered species of flora and fauna
(a) Fourteen biosphere reserves have been established in the country in which the species are protected. It is illegal to kill any animals in them.
(b) Project Tiger, Project Rhino and Project Great Indian Bustard have been started to help protect these endangered species.
(c) Many National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries have been set up in various parts of the country.
(d) Many awareness programmes like release of advertisements, conduct of seminars, etc are undertaken by the Government to sensitise the general public to these issues.
(iv) Describe how you can contribute to the protection of endangered animals and birds.
Answer We can contribute to protect the endangered animals and birds in the following ways
(a) If we find any illegal activity like poaching, trapping, etc being carried out in our area, we should report it to the Forest Department office in the area.
(b) We can conduct awareness programmes about wildlife preservation in our locality and community for all people.