GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Maths chapter 6 – Triangles
Back Exercise
Exercise 6.1
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks by using the correct word given in brackets.
(i) All circles are ……………. . (congruent/similar)
(ii) All squares are …………… . (similar/congruent)
(iii) All …………….. triangles are similar. (isosceles/equilateral)
(iv) Two polygons of the same number of sides are similar, if
(a) their corresponding angles are …………… and
(b) their corresponding sides are …………… (equal/proportional)
Solution:
Fill in the blanks.
(i) All circles are similar.
(ii) All squares are similar.
(iii) All equilateral triangles are similar.
(iv) Two polygons of the same number of sides are similar, if
(a) their corresponding angles are equal and
(b) their corresponding sides are proportional.
Question 2.
Give two different examples of pair of
(i) similar figures.
(ii) non-similar figures.
Solution:
(i) Examples of similar figures:
- Square
- Regular hexagons
(ii) Examples of non-similar figures:
- Two triangles of different angles.
- Two quadrilaterals of different angles.
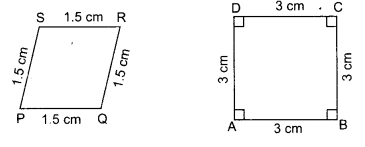
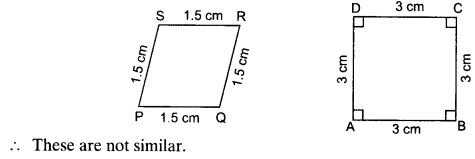
Question 3.
State whether the following quadrilaterals are similar or not.
Solution:
No, the sides of quadrilateral PQRS and ABCD are proportional but their corresponding angles are not equal.
Exercise 6.2
Question 1.
In the given figure (i) and (ii), DE || BC. Find EC in (i) and AD in (ii).
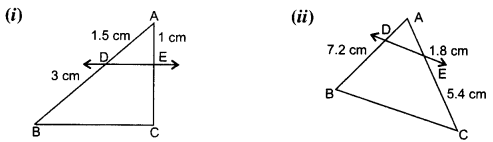
Solution:
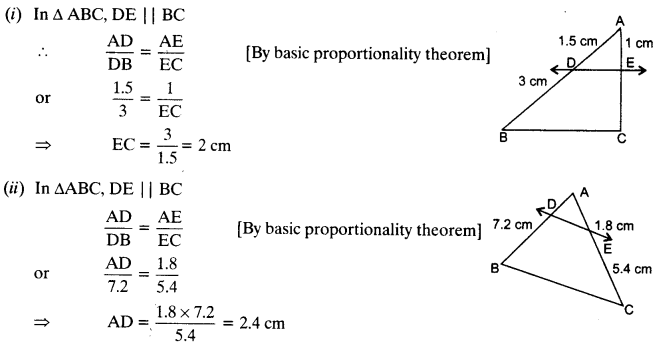
Question 2.
E and F are points on the sides PQ and PR respectively of a ∆PQR. For each of the following cases, state whether EF || QR:
(i) PE = 3.9 cm, EQ = 3 cm, PF = 3.6 cm and FR = 2.4 cm
(ii) PE = 4 cm, QE = 4.5 cm, PF = 8 cm and RF = 9 cm
(iii) PQ = 1.28 cm, PR = 2.56 cm, PE = 0.18 cm and PF = 0.36 cm
Solution:
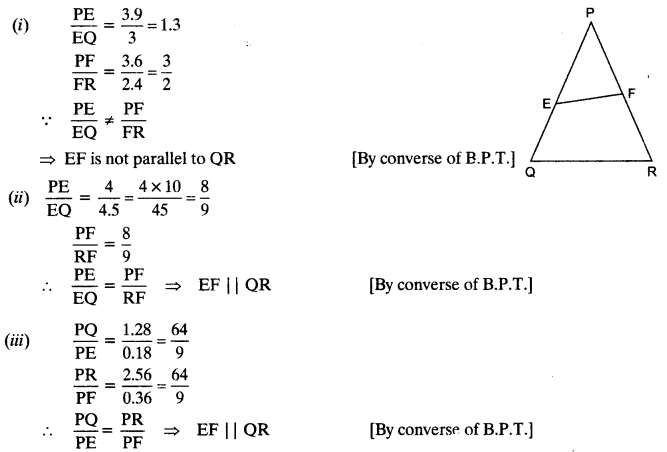
Question 3.
In the given figure, if LM || CB and LN || CD.
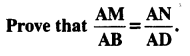
Solution:


Question 4.
In the given figure, DE || AC and DF || AE.
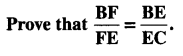
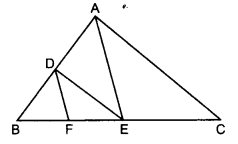
Solution:
Question 5.
In the given figure, DE || OQ and DF || OR. Show that EF || QR.
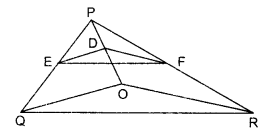
Solution:


Question 6.
In the given figure, A, B and C are points on OP, OQ and OR respectively such that AB || PQ and AC || PR. Show that BC || QR.
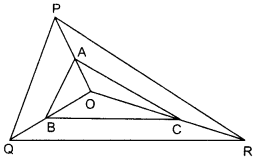
Solution:
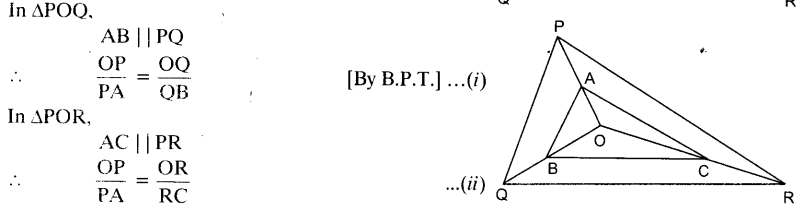
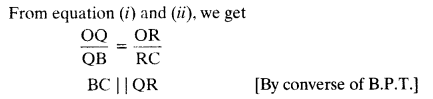
Question 7.
Using B.P.T., prove that a line drawn through the mid-point of one side of a triangle parallel to another side bisects the third side.
Solution:
Given: A ∆ABC in which D is the mid-point of AB and DE || BC

Question 8.
Using converse of B.P.T., prove that the line joining the mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side.
Solution:
Given: A ΔABC in which D and E are mid-points of sides AB and AC respectively.
To Prove: DE || BC
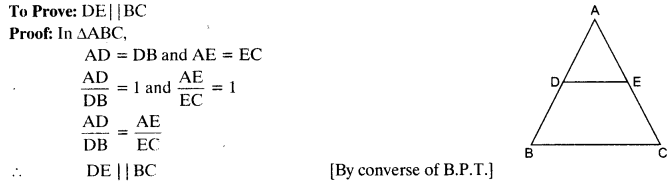
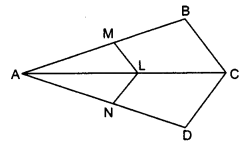
![]()
Question 9.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and its diagonals intersect each other at the
Solution:
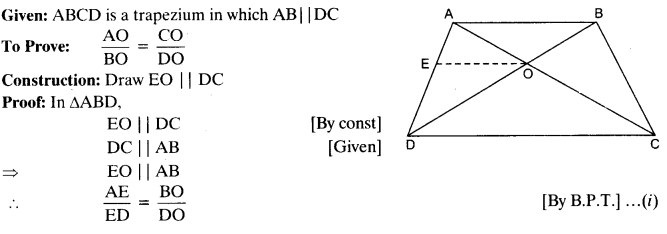
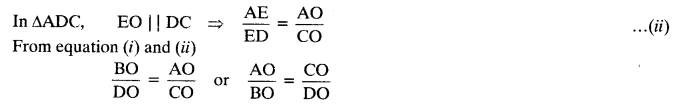
Question 10.
The diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point O such that
Solution:
Exercise 6.3
Question 1.
State which pairs of triangles in the given figures are similar. Write the similarity criterion used by you for answering the question and also write the pairs of similar triangles in the symbolic form :
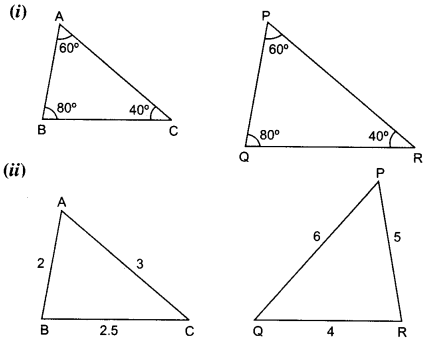
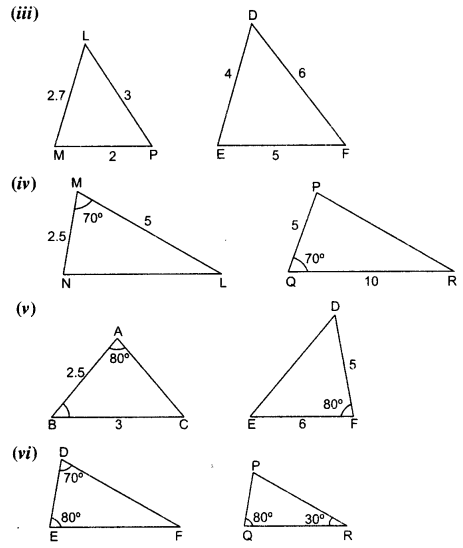
Solution:
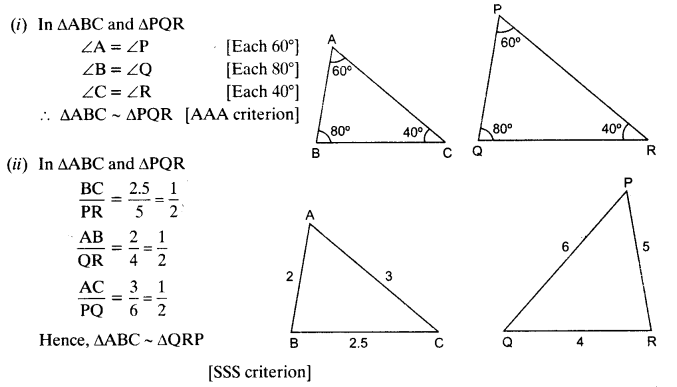
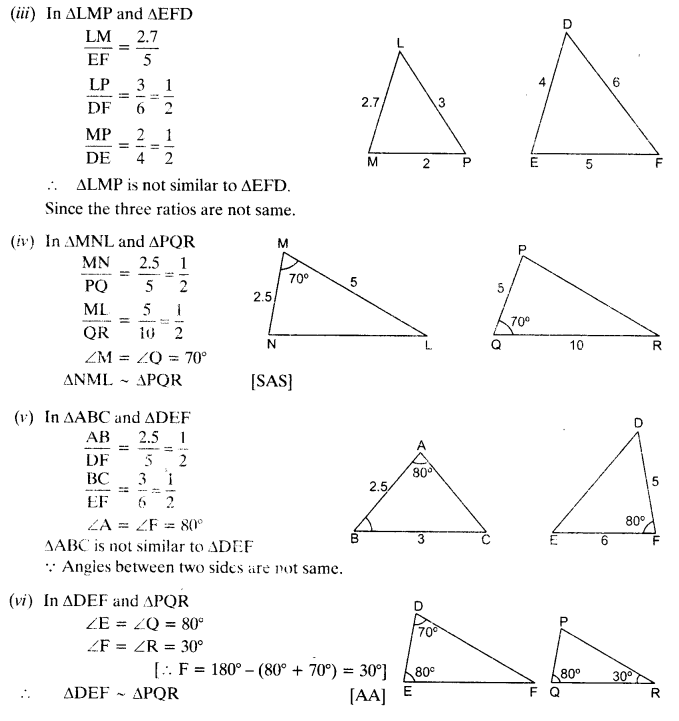
Question 2.
In the given figure, ∆ODC ~ ∆OBA, ∠BOC = 125° and ∠CDO = 70°. Find ∠DOC, ∠DCO and ∠OAB.
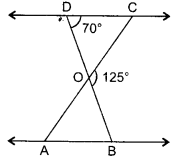
Solution:
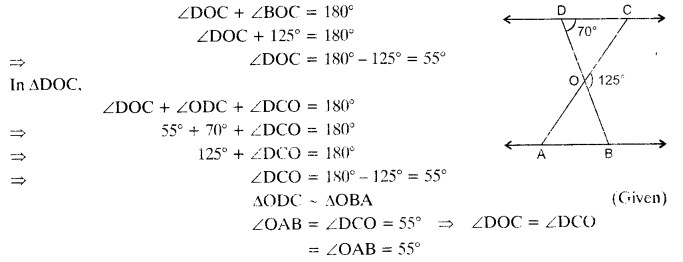
Question 3.
Diagonals AC and BD of a trape∠ium ABCD with AB || DC intersect each other at the point O. Using a similarity criterion for two triangles, show that
Solution:
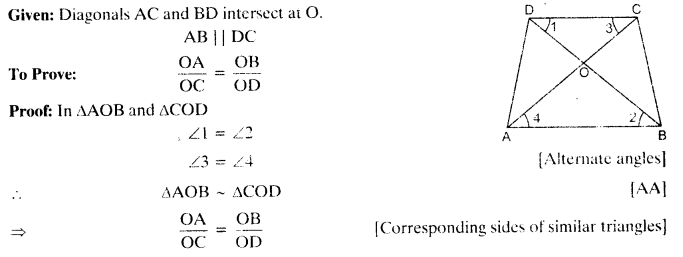
Question 4.
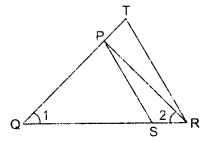
Solution:



Question 5.
S and T are points on sides PR and QR of ∆PQR such that ∠P = ∠RTS. Show that ∆RPQ ~ ∆RTS.
Solution:
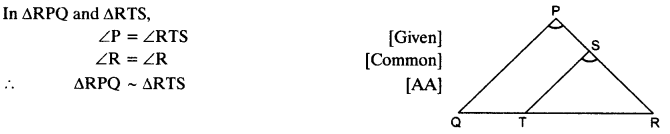
Question 6.
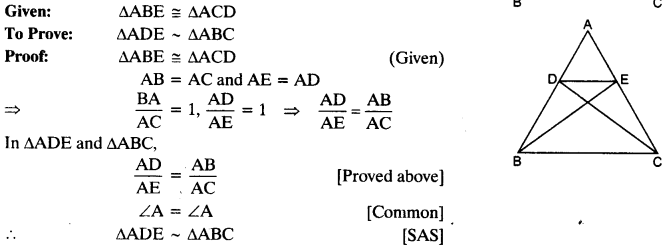
In the given figure, if ∆ABE ≅ ∆ACD, show that ∆ADE ~ ∆ABC.
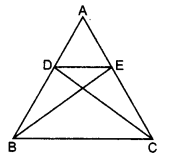
Solution:
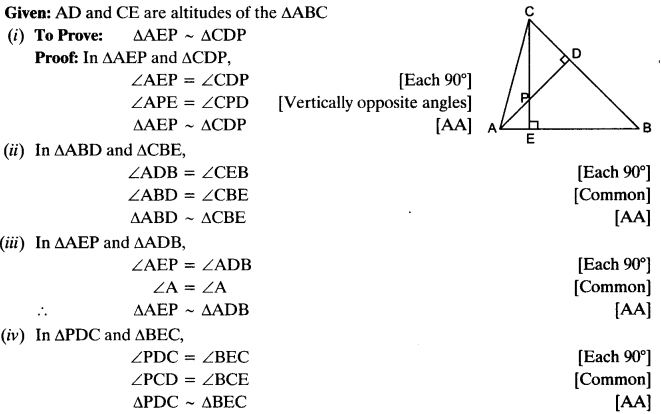
Question 7.
In the given figure, altitudes AD and CE of ∆ABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
(i) ∆AEP ~ ∆CDP
(ii) ∆ABD ~ ∆CBE
(iii) ∆AEP ~ ∆ADB
(iv) ∆PDC ~ ∆BEC
Solution:
Question 8.
E is a point on the side AD produced of a parallelogram ABCD and BE intersects CD at F. Show that ∆ABE ~ ∆CFB.
Solution:

Question 9.
In the given figure, ABC and AMP are two right triangles, right angled at B and M respectively. Prove that:
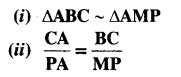
Solution:

Question 10.
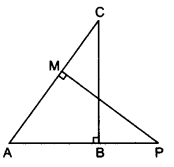
CD and GH are respectively the bisectors of ∠ACB and ∠EGF such that D and H lie on sides AB and FE of ∆ABC and ∆EFG respectively. If ∆ABC ~ ∆FEG, show that
![]()
Solution:
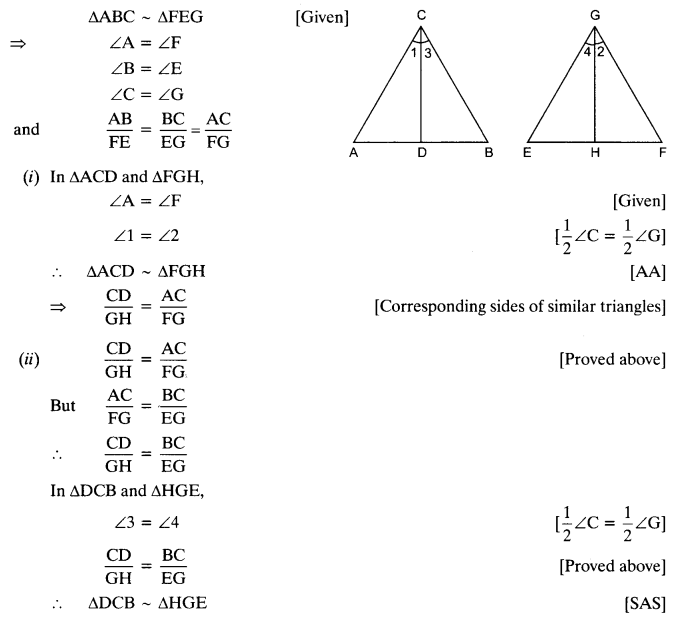

Question 11.
In the given figure, E is a point on side CB produced of an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. If AD ⊥ BC and EF ⊥ AC, prove that ∆ABD ~ ∆ECF.
Solution:
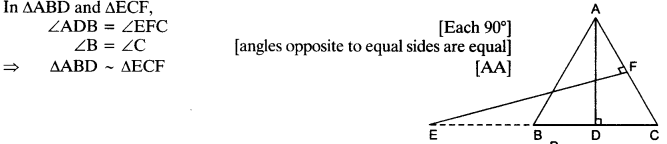
Question 12.
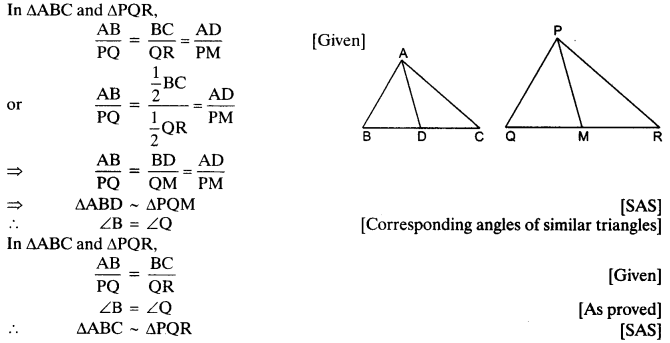
Sides AB and BC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and QR and median PM of ∆PQR (see in given figure). Show that ∆ABC ~ ∆bPQR.
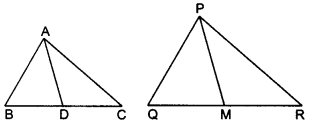
Solution:
Question 13.
D is a point on the side BC of a triangle ABC, such that ∠ADC = ∠BAC. Show that CA² = CB.CD.
Solution:

Question 14.
Sides AB and AC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and PR and median PM of another triangle PQR. Show that ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR.
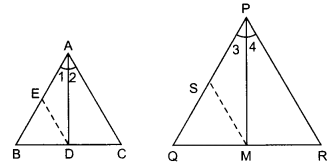
Solution:
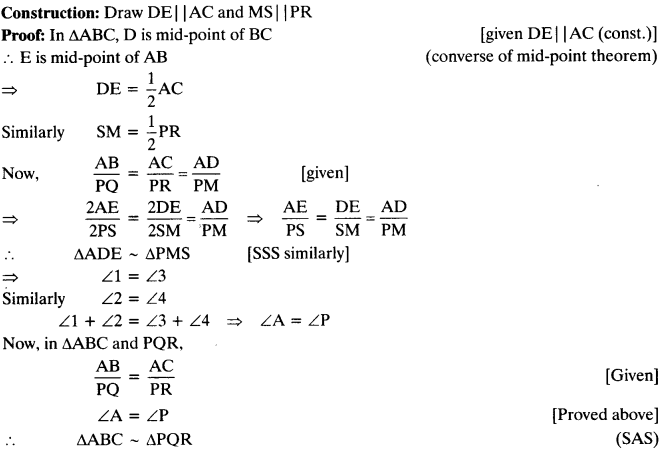
Question 15.
A vertical pole of length 6 m casts a shadow 4 m long on the ground and at the same time a tower casts a shadow 28 m long. Find the height of the tower.
Solution:
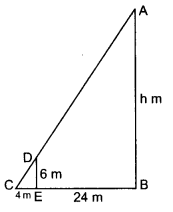
DE is a vertical pole of length = 6 m
Length of its shadow = 4 m
Let height of tower AB = h m
Length of its shadow = 28 m
In ∆ABC and ∆DEC,
∠ABC = ∠DEC [Each 90°]
∠C = ∠C [Common]
∆ABC ~ ∆DEC [AA]
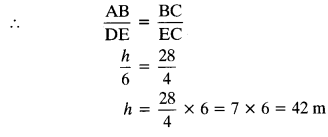
Question 16.
If AD and PM are medians of triangles ABC and PQR respectively, where
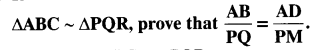
Solution:
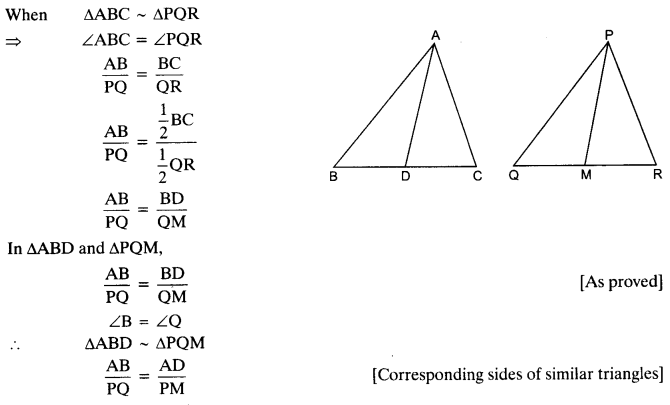
Exercise 6.4
Question 1.
Let ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF and their areas be, respectively, 64 cm2 and 121 cm2. If EF = 15.4 cm, find BC.
Solution:
Since, ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of the corresponding sides.
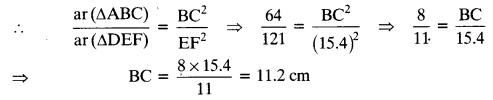
Question 2.
Diagonals of a trapezium ABCD with AB || DC intersect each other at the point O. If AB = 2 CD, find the ratio of the areas of triangles AOB and COD.
Solution:
ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC and AB = 2 CD
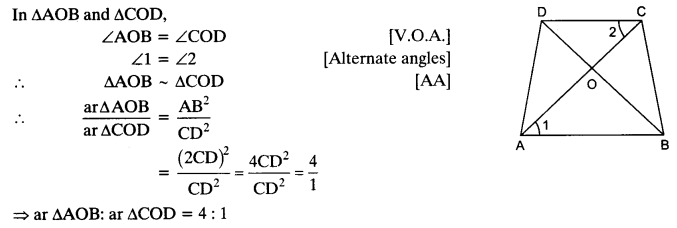
Question 3.
In the given figure, ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. If AD intersects BC at O, show that
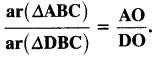
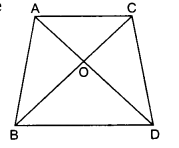
Solution:
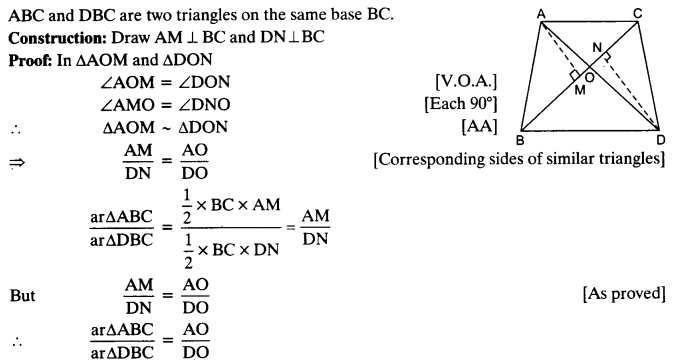
Question 4.
If the areas of two similar triangles are equal, prove that they are congruent.
Solution:
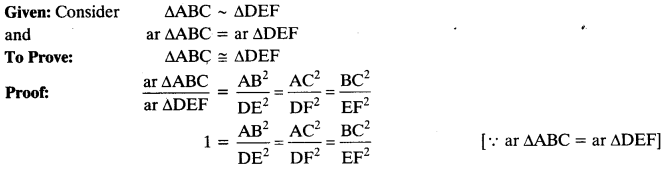
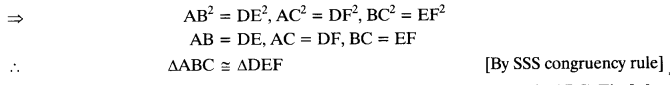
Question 5.
D, E and F are respectively the mid-points of sides AB, BC and CA of ∆ABC. Find the ratio of the areas of ∆DEF and ∆ABC.
Solution:

Question 6.
Prove that the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding medians.
Solution:
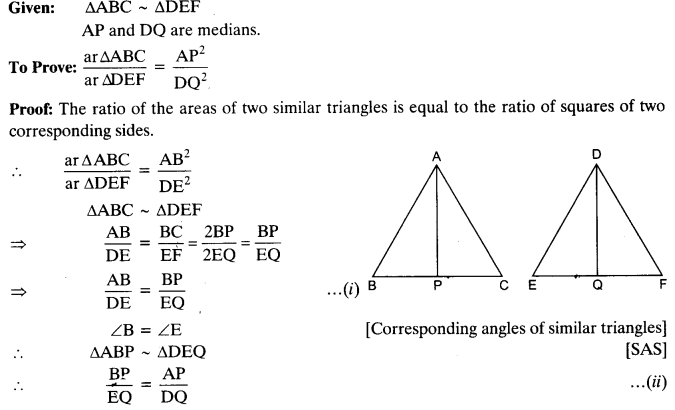
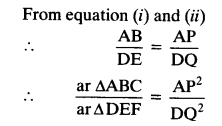
Question 7.
Prove that the area of an equilateral triangle described on one side of a square is equal to half the area of the equilateral triangle described on one of its diagonals.
Solution:
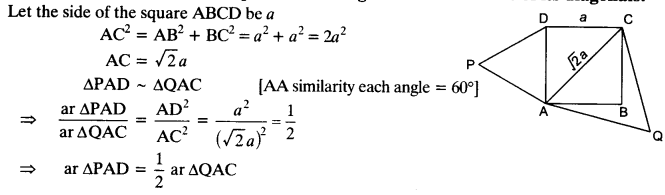
Question 8.
ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid-point of BC. Ratio of the areas of triangles ABC and BDE is
(a) 2 :1
(b) 1:2
(c) 4 :1
(d) 1:4
Solution:
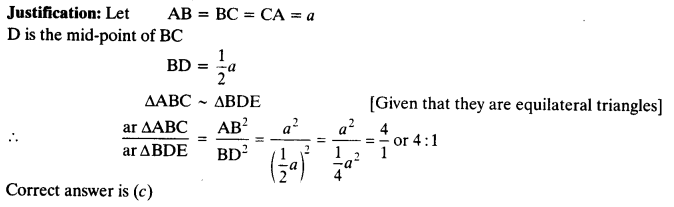
Question 9.
Sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio 4:9. Areas of these triangles are in the ratio
(a) 2:3
(b) 4:9
(c) 81:16
(d) 16:81
Solution:
Justification: Areas of two similar triangles are in the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides.
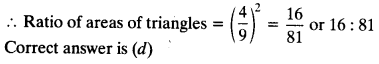
Exercise 6.5
Question 1.
Sides of triangles are given below. Determine which of them are right triangles. In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse.
(i) 7 cm, 24 cm, 25 cm (ii) 3 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm
(iii) 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm (iv) 13 cm, 12 cm, 5 cm
Solution:
(i) 7 cm, 24 cm,-25 cm
(7)2 + (24)2 = 49 + 576 = 625 = (25)2 = 25
∴ The given sides make a right angled triangle with hypotenuse 25 cm
(ii) 3 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm
(8)2 = 64
(3)2 + (6)2 = 9 + 36 = 45
64 ≠ 45
The square of larger side is not equal to the sum of squares of other two sides.
∴ The given triangle is not a right angled.
(iii) 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
(100)2= 10000
(80)2 + (50)2 = 6400 + 2500
= 8900
The square of larger side is not equal to the sum of squares of other two sides.
∴The given triangle is not a right angled.
(iv) 13 cm, 12 cm, 5 cm
(13)2 = 169
(12)2 + (5)2= 144 + 25 = 169
= (13)2 = 13
Sides make a right angled triangle with hypotenuse 13 cm.
Question 2.
PQR is a triangle right angled at P and M is a point on QR such that PM ⊥ QR. Show that PM2 = QM • MR.
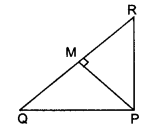
Solution:
In right angled ∆QPR,
∠P = 90°, PM ⊥ QR
∴ ∆PMQ ~ ∆RMP
[If ⊥ is drawn from the vertex of right angle to the hypotenuse then triangles on both sides of perpendicular are similar to each other, and to whole triangle]
⇒ [Corresponding sides of similar
⇒ PM x MP = RM x MQ ⇒ PM2 = QM.MR
Question 3.
In the given figure, ABD is a triangle right angled at A and AC i. BD. Show that
(i) AB2 = BC.BD
(ii) AC2 = BC.DC
(iii) AD2 = BD.CD
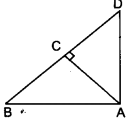
Solution:


Question 4.
ABC is an isosceles triangle right angled at C. Prove that AB2 = 2AC2.
Solution:
Given: In ∆ABC, ∠C = 90° and AC = BC
To Prove: AB2 = 2AC2
Proof: In ∆ABC,
AB2= BC2 + AC2
AB2 = AC2 + AC2 [Pythagoras theorem]
= 2AC2
Question 5.
ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. If AB2 = 2AC2 , Prove that ABC is a right triangle.
Solution:
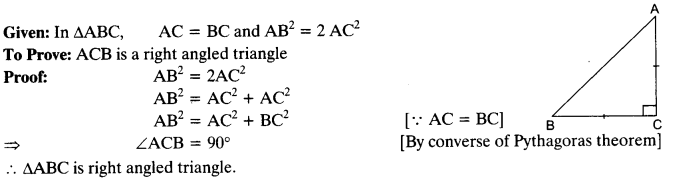
Question 6.
ABC is an equilateral triangle of side 2a. Find each of its altitudes.
Solution:
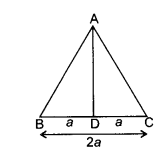
Given: In ∆ABC, AB = BC = AC = 2a
We have to find length of AD
In ∆ABC,
AB = BC = AC = 2a
and AD ⊥ BC
BD =
In right angled triangle ADB,
AD2 + BD2 = AB2
⇒ AD2 = AB2 – BD2= (2a)2 – (a)2 = 4a2– a2= 3a2
AD = √3a
Question 7.
Prove that the sum of the squares of the sides of a rhombus is equal to the sum of the squares of its diagonals.
Solution:
Given: ABCD is a rhombus. Diagonals AC and BD intersect at O.
To Prove: AB2+ BC2+ CD2+ DA2 = AC2+ BD2
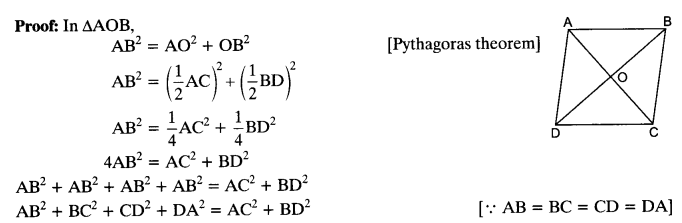
Question 8.
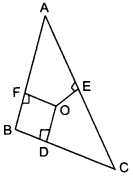
In the given figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD ⊥ BC, OE ⊥ AC and OF ⊥ AB. Show that
(i) OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2
(ii) AF2 + BD2 + CE2 = AE2 + CD2 + BF2.
Solution:

Question 9.
A ladder 10 m long reaches a window 8 m above the ground. ind the distance of the foot of the ladder from base of the wall.
Solution:
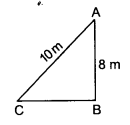
Let AC be the ladder of length 10 m and AB = 8 m
In ∆ABC, BC2 + AB2 = AC2
⇒ BC2= AC2 – AB2= (10)2 – (8)2
BC2 = 100-64 – 36 BC = √36 = 6 m
Hence distance of foot of the ladder from base of the wall is 6 m.
Question 10.
A guy wire attached to a vertical pole of height 18 m is 24 m long and has a stake attached to the other end. How far from the base of the pole should the stake be driven so that the wire will be taut?
Solution:
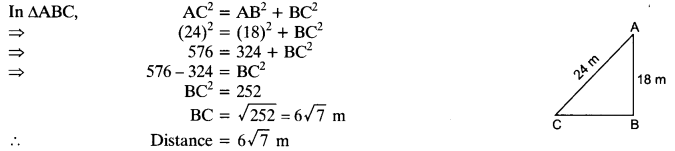
Question 11.
An aeroplane leaves an airport and flies due north at a speed of 1000 km per hour. At the same time, another aeroplane leaves the same airport and flies due west at a speed of 1200 km per hour. How far apart will be the two planes after 1
Solution:
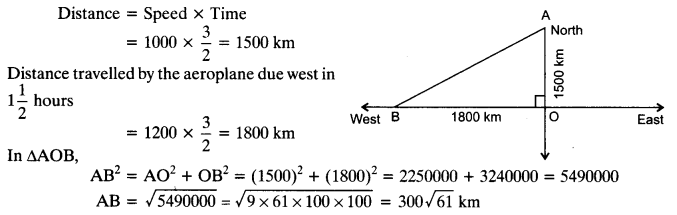
Question 12.
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the poles is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
Solution:
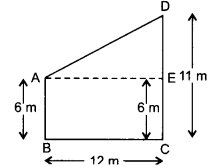
Length of poles is 6 m and 11m.
DE = DC – EC = 11m-6m = 5m
In ∆DAE,
AD2 = AE2 + DE2 [ ∵AE = BC]
= (12)2 + (5)2 =144 + 25 = 169
AD = √l69 = 13
Question 13.
D and E are points on the sides CA and CB respectively of a triangle ABC right angled at C. Prove that AE2 + BD2 = AB2 + DE2.
Solution:
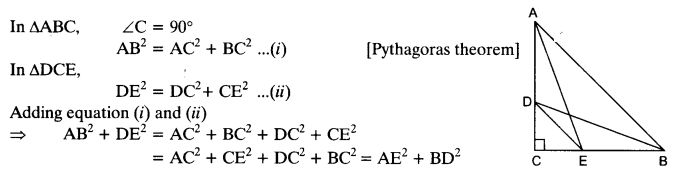
Question 14.
The perpendicular from A on side BC of a ∆ABC intersects BC at D such that DB = 3CD (see the figure). Prove that 2AB2 = 2AC2 + BC2.
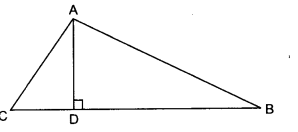
Solution:
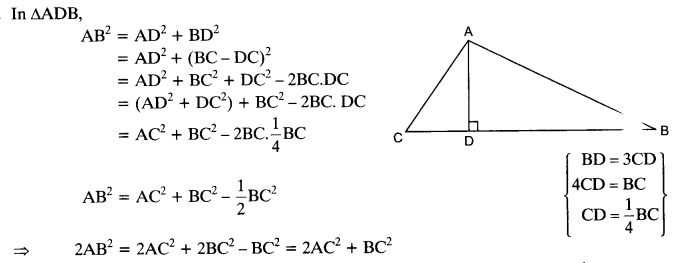
Question 15.
In an equilateral triangle ABC, D is a point on side BC, such that BD =
Solution:
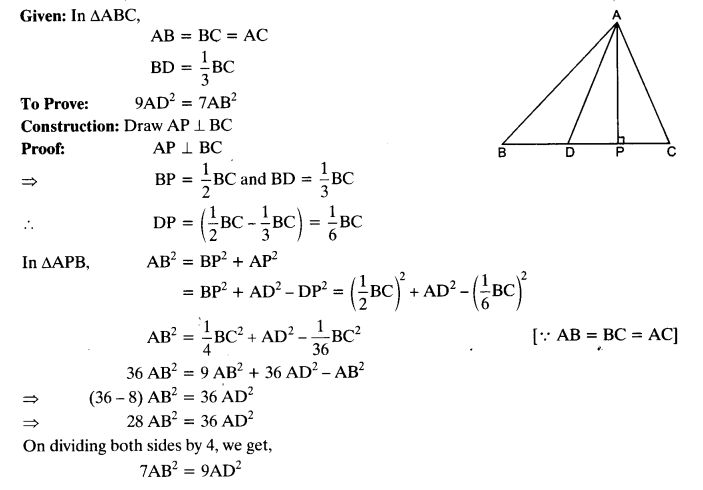
Question 16.
In an equilateral triangle, prove that three times the square of one side is equal to four times the square of one of its altitudes.
Solution:
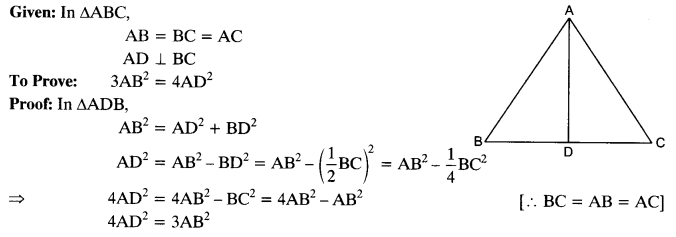
Question 17.
Tick the correct answer and justify : In ∆ABC, AB = 6√3 cm, AC = 12 cm and BC = 6 cm. The angle B is:
(a) 120°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 45
Solution:

Exercise 6.6
Question 1.
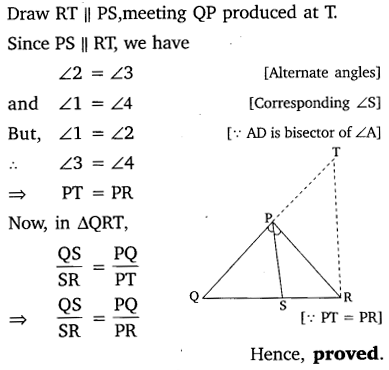
In the given figure, PS is the bisector of ∠QPR of ∆PQR. Prove that
 Solution:
Solution:
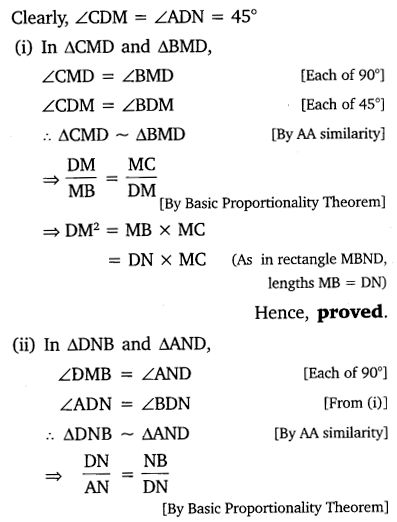
Question 2.
In the given figure, D is a point on hypotenuse AC of ∆ABC, DM ⊥ BC and DN ⊥ AB. Prove that:
(i) DM2 = DN X MC
(ii) DN2 = DM X AN
 Solution:
Solution:
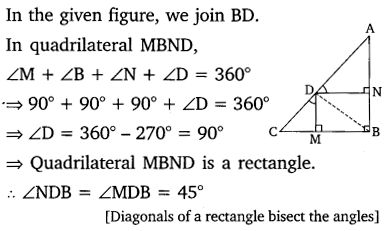
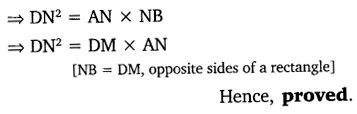
Question 3.
In the given figure, ABc is triangle in which ∠ABC > 90° and AD ⊥ CB produced. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC X BD
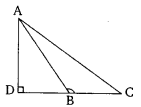 Solution:
Solution:
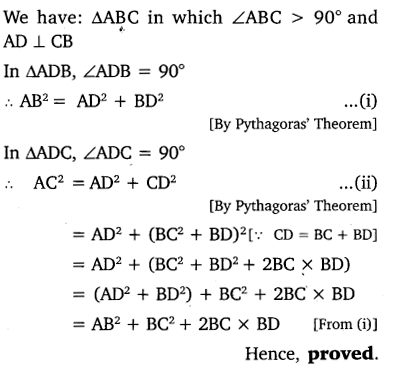
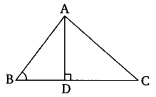
Question 4.
In the given figure, ABC is atriangle in which ∠ABC 90° and AD ⊥ CB. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 – 2BC X BD
 Solution:
Solution:
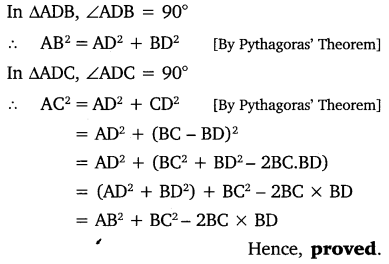
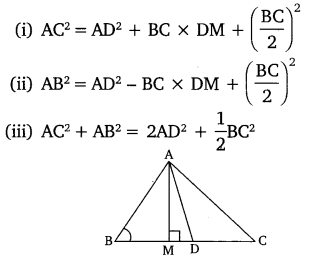
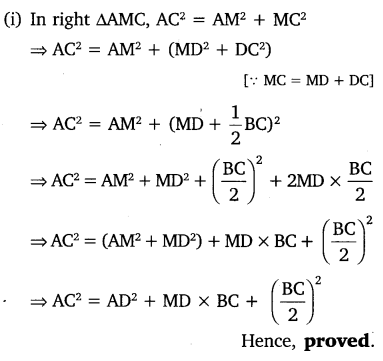
Question 5.
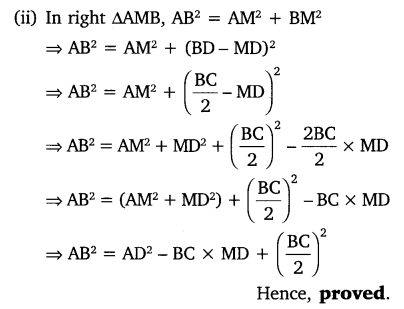
In the given figure, Ad is a median of a triangle ABC and AM ⊥ BC. Prove that
Solution:

Question 6.
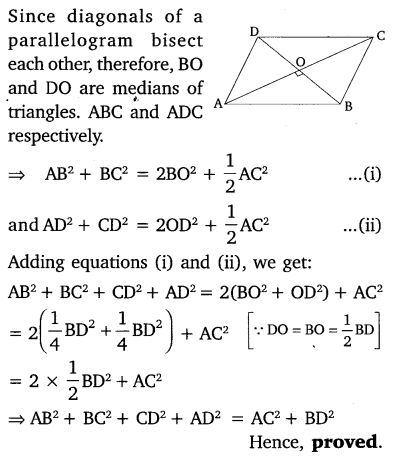
Prove that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of its sides.
Solution:
Question 7.
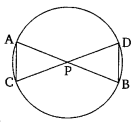
In the given figure, two chords AB and CD intersect each other at the point P. Prove that:
(i) ∆APC ~∆DPB
(ii) AP X PB = CP X DP
Solution:

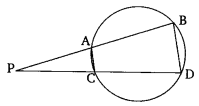
Question 8.
In the given figure, two chords Ab and CD of a circle intersect each other at the point P (when produced) outside the circle. Prove that:
(i) ∆PAC ~ ∆PDB
(ii) PA X PB = PC X PD
 Solution:
Solution:

Question 9.
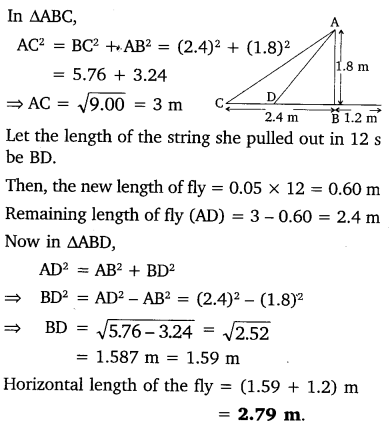
In the given figure, D is a point on side BC of ∆ABC, such that
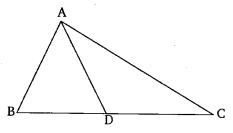 Solution:
Solution:
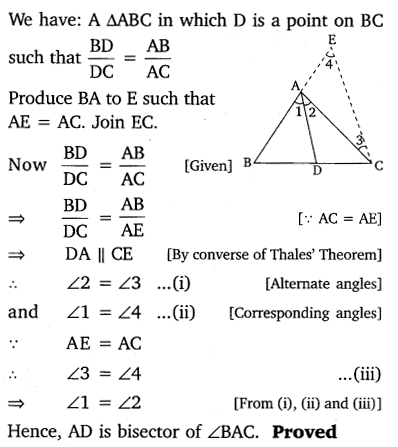
Question 10.
Nazima is fly fishing in a stream. The trip of her fishing rod is 1.8m above the surface of the water and the fly at the end of the string rests on the water 3.6m away and 2.4 m from a point directly under the trip of the rod. Assuming that her string (from the trip of the rod to the fly) is that, how much string does she have out (see the figure)? If she pills in the string at the rate of 5 cm per second, what will be the horizontal distance of the fly from her after 12 seconds?
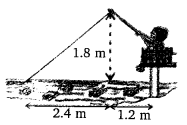 Solution:
Solution: