GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography chapter 6 – Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Back Exercise
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
- Which are the two factors on which the growth of vegetation mostly depends?
- Which are the three broad categories of natural vegetation?
- Name the two hardwood trees commonly found in tropical evergreen forest,
- In which part of the world is tropical deciduous forests found?
- In which climatic conditions are citrus fruits cultivated’?
- Mention the uses of coniferous forest.
- In which part of the world is seasonal grassland found?
Answer.
- The two factors on which the growth of vegetation mostly depends are— temperature and moisture.
- The three broad categories of natural vegetation are—forests, grasslands, and shrubs.
- Rosewood and mahogany.
- Tropical deciduous forests are found in a large part of India, northern Australia, and Central America.
- Citrus fruits are cultivated in the regions marked for hot dry summers and mild rainy winters.
- The woods of coniferous forests are tall and soft. Chir, pine, and cedar are the important variety of trees in these forests. The woods of these trees are very useful for making pulp, which is used for manufacturing paper and newsprint. Matchboxes and packing boxes are also made from softwood.
- Seasonal grasslands are found in the mid-latitudinal zones and in the interior parts of the continents.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) Mosses and Lichens are found in:
(a) Desertic Vegetation
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
(c) Tundra vegetation
Answer.
(c) Tundra vegetation
(ii) Thorny bushes are found in:
(a) Hot and humid tropical climate
(b) Hot and dry desertic climate
(c) Cold polar climate
Answer.
(b) Hot and dry desertic climate
(iii) In the tropical evergreen forest, one of the common animals is:
(a) Monkey
(b) Giraffe
(c) Camel
Answer.
(a) Monkey
(iv) One important variety of coniferous forest is:
(a) Rosewood
(b) Pine
(c) Teak
Answer.
(b) Pine
(v) Steppe grassland is found in:
(a) S. Africa
(b) Australia
(c) Central Asia
Answer.
(c) Central Asia
Question 3.
Match the following.
(i) Walrus (a) Softwood tree
(ii) Cedar (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest
(iii) Olives (c) A polar animal
(iv) Elephants (d) Temperate grassland in Australia
(v) Campos (e) Thorny shrubs
(vi) Downs (f) A citrus fruit
(g) Tropical grassland of Brazil
Answer.
(i) Walrus (c) A polar animal
(ii) Cedar (a) Softwood tree
(iii) Olives (f) A citrus fruit
(iv) Elephants (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest
(v) Campos (g) Tropical grassland of Brazil
(vi) Downs (d) Temperate grassland in Australia
Question 4.
Give Reasons.
- The animals in the polar region have thick fur and thick skin.
- Tropical deciduous trees shed their leaves in the dry season.
- The type and thickness of vegetation changes from place to place.
Answer.
- To protect themselves from the cold climatic conditions.
- To conserve water.
- Because of the variation in temperature, moisture, slope, and thickness of soil.
Question 5.
Activity.
(i) Collect pictures and photographs of forests and grasslands of different parts of the world. Write one sentence below each picture.
(ii) Make a collage of rainforest, grassland, and coniferous forests.
Answer.
(i) Pictures and Photographs of forests and grasslands:


The tidal forest supplies Sandalwood, a softwood ideal for making matches and packing material.
(ii) Now prepare a collage yourself with the help of your teacher.
Question 6.
For fun.
In the’ crossword table given below, some words are hidden. They are all about vegetation and wildlife and are to be found horizontally and vertically. Two have been worked out for you. Work in pairs with a friend.
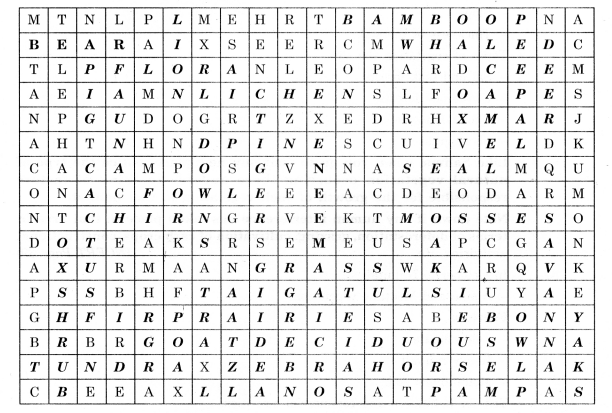
Answer.
Horizontally:
Bamboo, Bear, Whale, Flora, Lichen, Hen, Pine, Seal, Fowl, Chir, Mosses, Grass, Taiga, Tulsi, Prairie, Fir, Ebony, Goat, Deciduous, Tundra, Zebra, Horse, Lanos, Pampas,
Vertically:
Shrub, Ox, Pig, Cactus, Fauna, Lion, Downs, Tiger, Neem, Oak, Camel, Peepal, Owl, Deer, Savanna, Yak.
Do more exercise and find out other names of vegetation and wildlife. Elephant, Palm, Grebon.
In-Text Questions
Question 1.
Now can you tell why Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher? What type of vegetation did she see in the Himalayas starting with the foothills and going to the higher altitudes? (NCERT Page 39)
Answer.
Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher because of the following reasons:
- Change in a climate with an increase in height.
- Slope
- The thickness of the soil.
Types of vegetation she saw:
- Sal and teak forests
- Coniferous forests
- Rhodo-dendrous
- Short grass
Question 2.
Like Salima, when you go to visit any new place, notice the type of natural vegetation occurring there and try to think of factors responsible for the growth of such vegetation in that habitat.
Note down if any human interference has taken place in that area in terms of deforestation, grazing, cultivation of cash crops, construction activities, etc. (NCERT Page 39)
Answer.
In October to Nainital.
- Alpine and Montane vegetation.
Factors:
- Cold climate.
- Heavy rainfall.
- Mountainous soil.
Yes, for habitation and commercial activities.
Question 3.
Where in India do tropical evergreen and tropical deciduous forests occur? Name the states. (NCERT Page 41)
Which type of forest dominates most part of India?
Answer.
- Western slopes of western ghats, N.E. India—Tropical evergreen (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Goa, and N.E. states)
- Central India—Deciduous (M.P., Chhattisgarh), Jharkhand, etc.
- Tropical Deciduous.
Question 4.
Look around in your surroundings and find out the articles made of hardwood and softwood.
Find out and learn the names of few trees of your locality. (NCERT Page 43)
Answer.
Hardwood: Steppers, bridges, furniture, doors, windows.
Softwood: Matches, packing material, false ceiling, boats, etc.
Mango, neem, jamun, shisham, kikar, peepal, sal.
Question 5.
Can you name the great desert of India? Name some of the common animals of the desert. (NCERT page 44)
Answer.
Thar is the great Indian desert.
Camel, Snakes, lizards, and many insects are found here.