GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography chapter 6 – Population
Back Exercise
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below :(a) the area of departure
(c) the area of arrival
(ii) A large proportion of children in a population is a result of
(a) high birth rates
(c) high death rates
(iii) The magnitude of population growth refers to:
(a) the total population of an area
(b) the number of persons added each year
(c) the rate at which the population increases
(d) the number of females per thousand males
► (b) the number of persons added each year
(iv) According to the Census 2001, a literate person is one who
(a) can read and write his/her name
(b) can read and write any language
(c) is 7 year old and can read and write any language with understanding
(d) knows 3 Rs (reading, writing, arithmetic)
► (c) is 7 year old and can read and write any language with understanding
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Why is the rate of population growth in India declining since 1981?
(ii) Discuss the major components of population growth.
(iii) Define age structure, death rate and birth rate.
Answer
(i) The rate of population growth has been declining as a result of greater use of birth control measures.
(ii) The major components of population growth are Birth Rate, Death Rate and Migration. The difference between birth rate and death rate accounts for natural increase in population. Immigration refers to the inflow of people into a region from other regions.
(iii) The age structure of a population refers to the number of people in different age groups in that population.
Birth rate is the number of live births per thousand persons in a year.
Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year.
(iv) Migration is the movement of people across regions and territories. It is a determinant factor of population change as it changes the demographics (size and composition) of both the areas of departure and arrival.
3. Distinguish between population growth and population change.
Answer
Population Growth
|
Population Change
|
| It refers to the increase in the number of inhabitants of a region during a specific period of time. | It refers to the change in the distribution, composition or size of a population during a specific period of time. |
| Natural increase of population and immigration are the major components causing population growth. | Natural increase, immigration and emigration are the major components causing population change. |
4. What is the relation between occupational structure and development?
Answer
Development is related to occupational structure of the population. Countries are less developed where a higher percentage of population is engaged in primary occupations like agriculture, animal husbandry, forestry and fishing.
As development takes place more people move into secondary occupations like manufacturing.In highly developed societies, there are a high percentage of people involved in tertiary occupations like banking, commerce, transport and administration.
5. What are the advantages of having a healthy population?
Answer
The advantages of having a healthy population are:
→ A healthy individual is much more efficient and productive than an unhealthy individual.
→ He or she is able to realise his or her potential, and play an important role in social and national development.
→ Absenteeism is low where the workers are healthy.
6. What are the significant features of the National Population Policy 2000?
Answer
The National Population Policy 2000 provides a policy framework for:
→ Imparting free and compulsory school education up to 14 years of age.
→ Reducing infant mortality rate to below 30 per 1000 live births.
→ Achieving universal immunisation of children against all vaccine-preventable diseases.
→ Promoting delayed marriage and child bearing.
→ Making family welfare a people-centred programme.
→ Providing nutritional services and food supplements to adolescents.
→ Protecting adolescents from unwanted pregnancies and sexually-transmitted diseases, and educating them about the risks of unprotected sex.
→ Making contraceptive services accessible and affordable.
In-Text Questions
Page 54
Question 1. What could be the reason of uneven distribution of population in India?
Answer India has uneven distribution of population due to several factors like
(a) Low birth and high death rates areas.
(b) Topography Rugged terrain and unfavourable climatic conditions are primarily responsible for sparse population in states like Rajasthan and the hill states.
(c) Hilly, dissected and rocky nature of the terrain, moderate to low rainfall, shallow and less fertile soil are responsible for lesser population.
Question 2. Study the figure 6.3 and compare it with figure 2.4 and figure 4.7. Do you find any corelation between these maps?
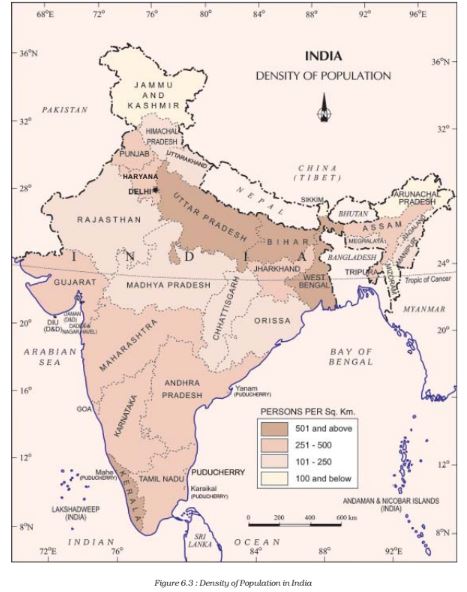
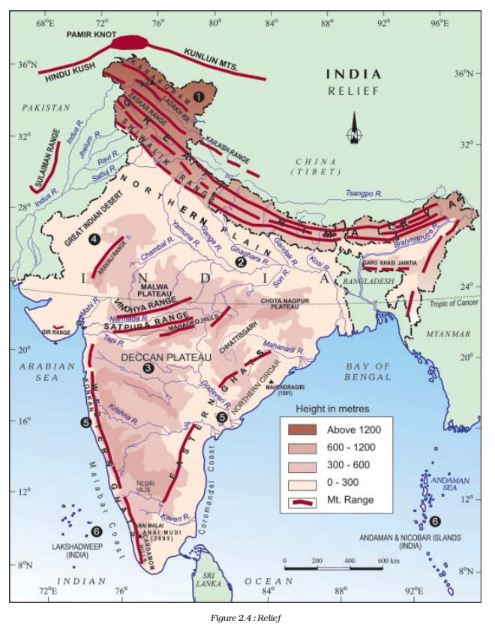
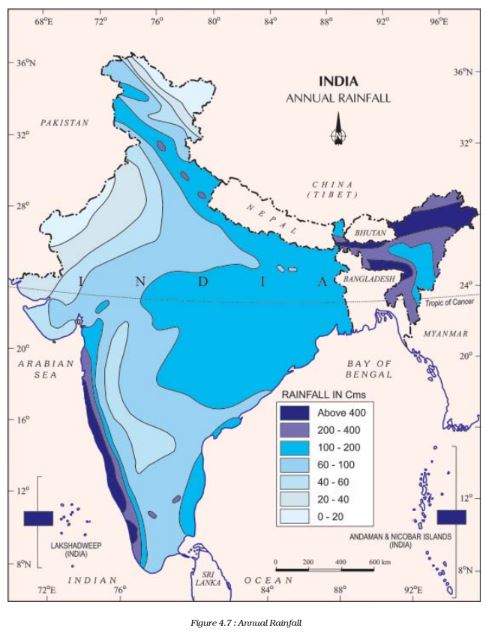
Answer Yes, these maps show that the nature of relief and amount of rainfall act as determinants of the population density in an area. The areas with high density of population (501 and above persons per sq km) are those areas which are the plains and having high rainfall. Such areas are good for agriculture and so more people live in these areas. The areas with least population (100 and below persons per sq km) are hilly areas and so mostly unsuitable for habitation.
Page 56
Question 1 Table 6.1 reveals that despite the decline in growth rates, the number of people being added every decade is steadily increasing. Why?
Table 6.1
| Year | Total population | Absolute increase in the decade | Annual growth rate (%) |
| 1951 | 361 | 42.43 | 1.25 |
| 1961 | 439.2 | 78.15 | 1.96 |
| 1971 | 548.2 | 108.92 | 2.20 |
| 1981 | 683.3 | 135.17 | 2.22 |
| 1991 | 846.4 | 163.09 | 2.14 |
| 2001 | 1028.7 | 182.32 | 1.93 |
Answer The number of people increasing every decade population at beginning of the decade X Growth rate. Since the total population is growing every decade, even though the growth rate is reducing, it is not able to offset the increased total population, i.e., base population. So, the number of people being added every decade is steadily increasing.
Page 58
Question 2. Kerala has a sex ratio of 1058 females per 1000 males. Pondicherry has 1001 females 1000 males, while Delhi has 821 females per 1000 males and Haryana has just 861 females. What could be the reasons for such variation?
Answer Kerala and Pondicherry have a sex ratio of more than 1000 females per 1000 males while Delhi has 821 females per 1000 males and Haryana just 861 females because
(a) Kerala and Pondicherry have good health facilities, which reduces infant mortality.
(b) These states have higher literacy rates. Due to higher literacy of women, they are understanding the advantages of small families.
(c) In Delhi, there is a heavy migration of males who get jobs in the metropolis. Generally, their families stay back in their villages or home towns. This leads to a very high number of males in Delhi.
(d) In Haryana, female foeticide is rampant because of people’s desire to have a male heir, due to a patriarchal family system. This has led to the skewed sex ratio in Haryana.