GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science chapter 7 – Control and Coordination
Back Exercise
Question 1.
Which of the following is a plant hormone ?
(A) Insulin
(B) Thyroxine
(C) Oestrogen
(D) Cytokinin.
Answer:
(D) Cytokinin
Question 2.
The gap between two neurons is called
(A) Dendrite
(B) Synapse
(C) Axon
(D) Impulse.
Answer:
(B) Synapse
Question 3.
The brain is responsible for
(A) Thinking
(B) Regulating the heart beat
(C) Balancing
(D) All the above.
Answer:
(D) All the above
Question 4.
What is the function of receptors in our body ? Think of situation where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Receptors are specialised cells, tissues, organs and nerve endings which are able to pick up specific stimuli, e.g., photoreceptors, gustatoreceptors, thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, statoreceptors, tangoreceptors, pain and pressure receptors. Receptors provide sensory input about external and internal environment. Without them, an animal will not able to observe, handle and taste food. It will not be aware of an approaching enemy. The animal may not be able to correct its position and fall down repeatedly if its statoreceptors are damaged. Therefore, the animal will not be able to perform the activities connected with the defective receptors.
Question 5.
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its functions. (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
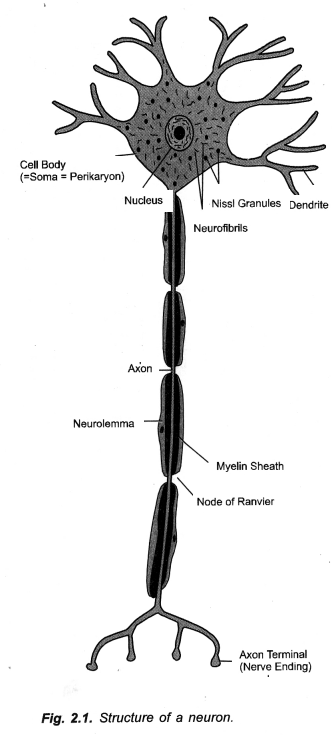
Functions:
- Dendrites. Picking up sensations and transmitting the same to cell body.
- Cell Body,
- Sustaining structure and function of dendrites and axon,
- Functioning as passage¬way for transmission of sensation or impulse to axon.
- Axon. Carrying impulse to another neuron, muscle, gland and organ. A single impulse can be transmitted to several structures with the help of axon terminals.
Question 6.
How does phototropism occur in plants ?
Answer:
It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to unidirectional exposure to light. The region of photoperception is shoot apex while the region of response is in the area of elongation. The light effective in phototropic response is blue light. The photoreceptor is a flavoprotein called phototropin. Leaves are essential for producing the response.
Stems generally bend towards the direction of light. They are positively phototropic. Leaves generally come to lie at right angles to light. They are diaphototropic. Roots are either neutral (non-phototropic) or negatively phototropic. Positively phototropic heads of Sunflower perform solar tracking as they move from east to west along the direction of sun.
Phototropic movement is generally caused by increased auxin on the dark side and lesser auxin on the illuminated side. It causes more growth on the dark side of stem causing it to bend towards the source of light. The opposite happens in root where less auxin stimulates growth while higher auxin inhibits growth.
In the plant growing in the open, sunlight is received from above. Auxin diffuses equally on all sides so that the stem does not bend but grows straight vertically.
Question 7.
Which signals will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury ?
Answer:
- Sensory impulses from the area innervated by injured portion,
- Transmission of motor impulses through the injured portion,
- Reflex action in the area of injury. Sensations and movements are restricted.
Question 8.
How does chemical coordination occur in plants ?
Answer:
Plants do not have nervous system but still sense the things because of stimulus such as gravity, light, chemicals(hormones), water, touch (touch -me -not plant).Hormones are responsible for the chemical coordination of plants by integrating their behaviour by affecting growth of a plant resulting in movement of that plant part in response to a stimulus. When sunlight falls on the shoot from one side, the auxins hormone causes the shady side of the shoot to grow faster, making the shoot bend towards sunlight.
Question 9.
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism ?
Answer:
Controlled movement must be connected to the recognition of various events in the environment, followed by only the correct movement in response. In other words, living organisms must use systems providing control and coordination. In keeping with the general principles of body organisation in Multicellular organisms, specialised tissues are used to provide these control and coordination activities.
(i) Coordination is needed for all human activities like, thinking and behaviour. Our breathing process, hearts beats, we dance, read, write by the action of our nervous system. Our nervous system gets information from surroundings and processes it and then respond according to it. The endocrine system (hormonal system) helps in integrating various metabolic activities like reproduction, development, all reflex actions (cope up with various give up situations).
(ii)The hormonal system in plants helps in process of photosynthesis; they need carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The stomatal opening in leaves opens up to allow in carbon dioxide gas, the roots bend towards water and the stem grows towards sunlight, the tendrils in climbing pants are supported by the hormonal system of the plant body.
Thus, we have need of control and coordination system in an organisms.
Question 10.
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other ?
Answer:
| Reflex actions | Involuntary actions |
| 1. Rapid automatic responses to a stimulus without the conscious involvement of the brain | 1. Occurs without the consciousness of an organism |
| 2. Controlled by spinal cord | 2. Controlled by mid brain or medulla oblongata |
| 3. Very quick and instantaneous | 3. Relatively slower |
| 4. May involve any muscle or a gland | 4. Involves only smooth muscles |
| 5. Can be conditioned | 5. Cannot be influenced by external conditioning |
| Examples: Blinking of eyes, salivation | Examples: Beating of heart, blood circulation |
Question 11.
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
Nervous system Hormonal system
1. Made up of neurons (nerve cell).
1. Made of secretory cells (glands).
2. Messages transmitted in the form of electrical impulses.
2. Messages transmitted in the form of chemicals called hormones.
3. Messages transmitted along nerve fibre.
3. Messages transmitted along blood stream.
4. Effect of message usually lasts for a very short while.
4. Effect of message usually lasts longer.
5. Messages travel very quickly. 5. Messages travel more slowly.
Question 12.
What is the difference between the manner in which movement in Sensitive Plant and movement in our legs takes places ?
Answer:
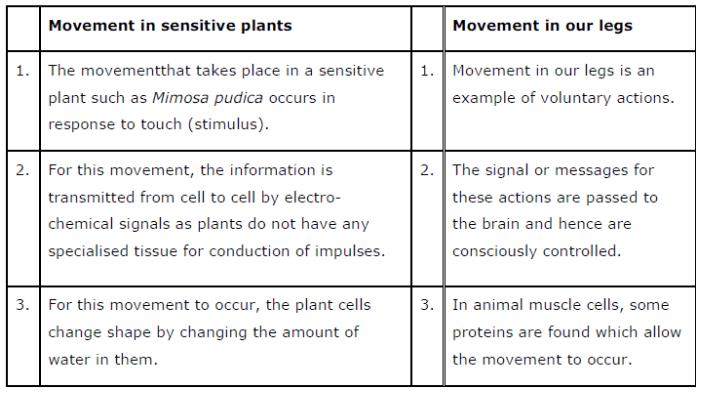
In-Text Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between reflex action and walking ?
Answer:
Walking is a voluntary action controlled by brain involves central nervous system and spinal cord both and affected by our thinking.
Question 2.
What happens at the synapse between two neurons ?
Answer:
The synapse is the tiny gap (not seen by naked eyes) between two adjacent neurons. This information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is the process how nervous impulses travel in the body. Similar synapse finally allows delivery of such impulses from neurons to other cells, such as muscles cells or gland.
Question 3.
Which part of brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body ?
Answer:
Cerebellum.
Question 4.
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick) ?
Answer:
When agarbatti burns, it produces pleasant smell, which is detected by the olfactory receptor present inside the nose. The action of smell generates the electrical impulse. These impulses are carried to the sensory area of brain(forebrain-cerebrum). Thus we detect the smell of agarbatti.
Question 5.
What is the role of brain in reflex action ? (CCE 2010, 2015)
Answer:
Reflex actions are formed instantaneously in response to the stimulus that has no time to think. For instance the sensory nerves that detect the heat are connected to the nerves that move the muscles of the hand. Such a connection of detecting the signal from the nerves (input) and responding to it quickly (output) is known as reflex arc.
Reflex action are generated in spinal cord and the information also reaches brain. This helps the brain to record this event and remember it for future use. Brain helps the person to get awareness of the stimulus and prevent himself from that situation again.
Question 6.
What are plant hormones ?
Answer:
The chemical substances produced in plants which control growth, development and responses in plants, are called plants plant hormones.
Question 7.
How is movement of leaves of Sensitive Plant different from movement of shoot towards light ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
| Movement of leaves of the sensitive plant | Movement of a shoot towards light |
| It does not depend on the direction of stimulus applied. | Depends on the direction of stimulus applied. |
| Called as Nastic movement | Called as tropic movement |
| Touch is the stimulus | Light is the stimulus |
| Caused by the sudden loss of water from the swellings at the base of leaves | Caused by the unequal growth on the two sides of the shoot. |
| Not a growth movement | Growth movement |
| Occurs very fast | Occurs slowly |
Question 8.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth ?
Answer:
Indole 3-acetic acid or IAA (auxin).
Question 9.
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Auxins are the plant hormones produces at the tip of a shoot and root. Auxins are present at the tip of tendrils. When tendrils are attached around any support their growth is slowed down as auxins are sensitive to touch. This make them move to the other side of the tip to get support this makes the other side grow faster than the side of tendril in contact with the support and the tendril bends towards the support.
Question 10.
Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism. (CBSE 2010, CCE 2011)
Answer:
Hydro’ means water. Hydrotropism means growth towards water.

Materials Required: Seed, A big container, Porous water pot, water and Sand.
Procedure:
• The tray should be big enough to accommodate the porous pot.
• Fill the tray with sand and insert some seeds in it.
• Make a pit in the sand and insert the porous pot in it.
• Fill the porous pot with water. • Leave the set up for about a week.
Observation:
After a week when seeds are taken out, it is observed that roots grow in the direction of the porous pot. This shows hydrotropic movement in roots.
Question 11.
How does chemical coordination take place in animals ?
Answer:
The chemical coordination in animals takes place by the action of chemical called hormones. They are produced in certain glands in body in very small amount and poured directly in the blood. They are target based means works on particular organs and these organs are called target organs. The hormones control and coordinate various functions of the body such as development, growth, sexual changes etc.
Question 12.
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable ? (CCE 2011, 2015)
Answer:
Iodine is essential for synthesis of hormone thyroxine in thyroid gland. Thyroxine controls basal metabolic rate, physical activity, body temperature, heart beat, mental, physical and sexual development besides regulating carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. Deficiency of thyroxine disturbs metabolic, physical and mental activities besides causing disorders of simple goitre, cretinism and myxedema. Therefore, it is always advisable to take iodised salt so that there is no deficiency of iodine.
Question 13. Question 14.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into blood ?
Answer:
Adrenaline is secreted directly into the blood and carried to different parts of the body. The target organs or the specific tissues on which it acts include the heart. As a result, the heart beats faster, resulting in supply of more oxygen to our muscles. The blood to the digestive system and skin is reduced due to contraction of muscles around small arteries in these organs. This diverts the blood to our skeletal muscles. The breathing rate also increases because of the contractions of the diaphragm and the rib muscles. All these responses together enable the animal body to be ready to deal with the situation. Such animal hormones are part of the endocrine system which constitutes a second way of control and coordination in our body.
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin ?
Answer:
Diabetes mellitus is of two types, insulin dependent and insulin independent. In insulin dependent diabetes, pancreas is unable to produce required quantity of insulin. As a result blood sugar continues to rise and part of sugar is excreted through urine resulting in diabetes. This is kept under check by regular injection of insulin. Availability of insulin will help the cells to take up glucose while liver and muscles are induced to store excess of glucose as glycogen.