GetStudySolution
Getstudysolution is an online educational platform that allows students to access quality educational services and study materials at no cost.
NCERT Solutions for class 10 Maths chapter 8 – Introduction to Trigonometry
Back Exercise
Exercise 8.1
Question 1.
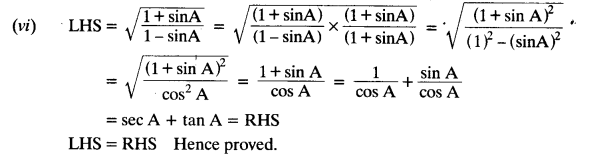
In ∆ABC right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine:
(i) sin A, cos A
(ii) sin C, cos C
Solution:
Question 2.
In given figure, find tan P – cot R.
Solution:

Question 3.
If sin A =
Solution:
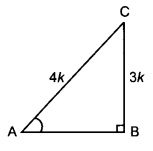
sin A =
sin A =
Let BC = 3k and AC = 4k
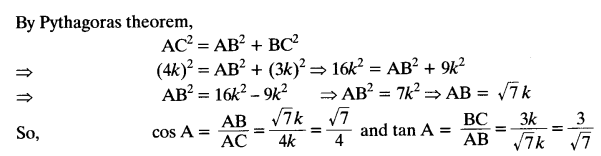
Question 4.
Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
Solution:
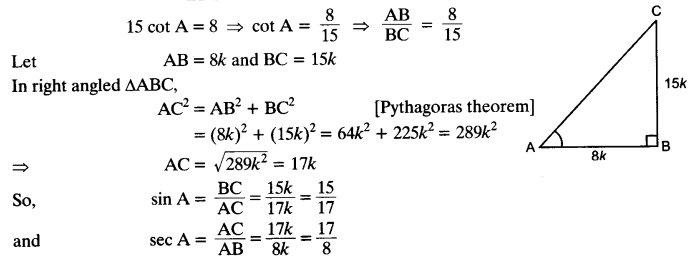
Question 5.
Given sec θ =
Solution:
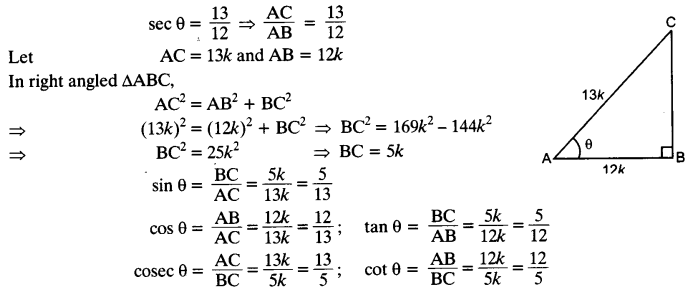
Question 6.
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
Solution:

Question 7.
If cot θ =
(i)
(ii) cot²θ
Solution:
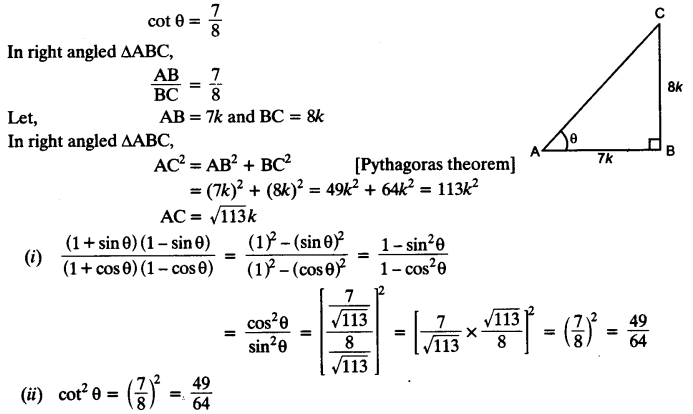
Question 8.
If 3 cot A = 4, check whether
Solution:
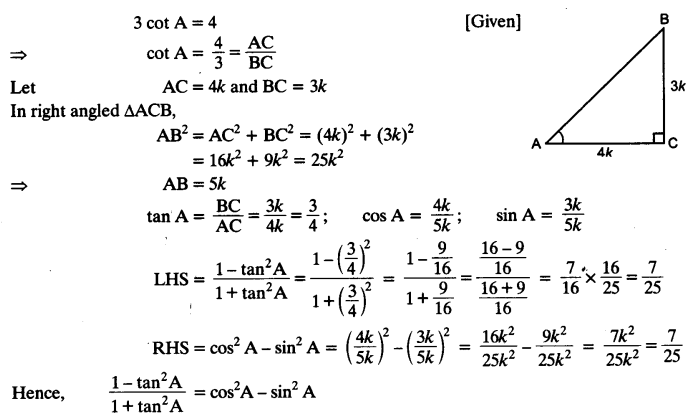
Question 9.
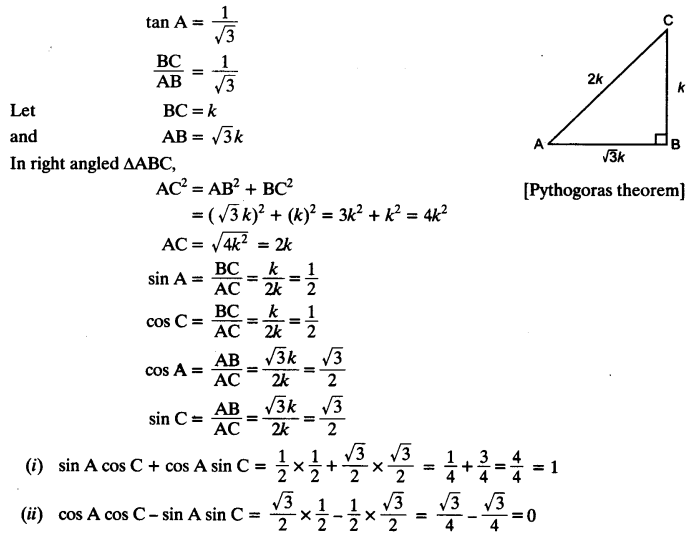
In triangle ABC, right angled at B, if tan A =
(i) sin A cos C + cos A sin C
(ii) cos A cos C – sin A sin C
Solution:
Question 10.
In ΔPQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
Solution:


Question 11.
State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
(ii) sec A =
(iii) cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
(iv) cot A is the product of cot and A.
(v) sin θ =
Solution:
(i) tan 60° = √3 , Since √3 > 1. (False)
(ii) sec A is always ≥ 1. (True)
(iii) cos A is the abbreviation for cosine A. (False)
(iv) cot without ∠A is meaningless. (False)
(v) sin θ can never be greater than 1.
∴ sin θ =
Exercise 8.2
Question 1.
Evaluate the following:
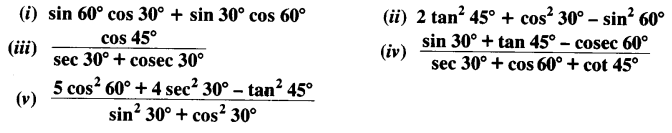
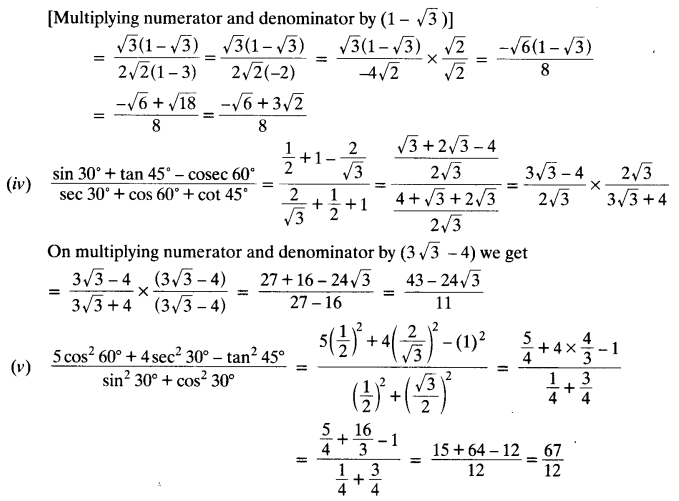
Solution:
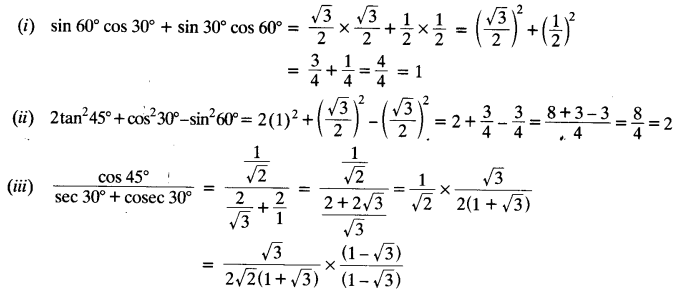
Question 2.
Choose the correct option and justify your choice:

Solution:
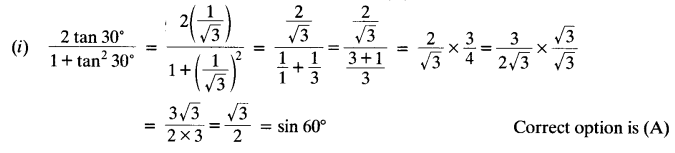
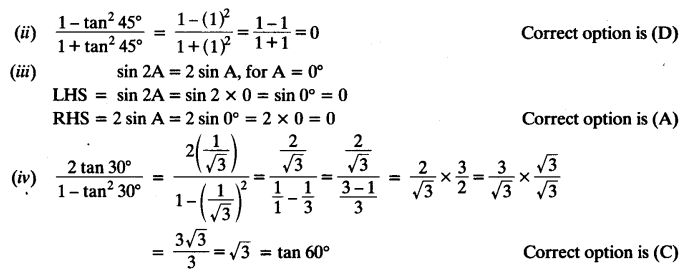
Question 3.
If tan (A + B) = √3 and tan (A – B) =
Solution:
tan (A + B) = √3
⇒ tan (A + B) = tan 60°
⇒ A + B = 60° ……(i)
tan (A – B) =
⇒ tan (A – B) = tan 30°
⇒ A – B = 30° ……..(ii)
Adding equation (i) and (ii), we get
2A = 90° ⇒ A = 45°
From (i), 45° + B = 60° ⇒ B = 60° – 45° = 15°
Hence, ∠A = 45°, ∠B = 15°
Question 4.
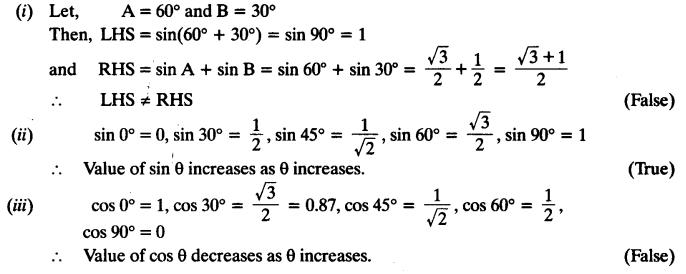
State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A + sin B.
(ii) The value of sin θ increases as θ increases.
(iii) The value of cos θ increases as θ increases.
(iv) sin θ = cos θ for all values of θ.
(v) cot A is not defined for A = 0°.
Solution:

Exercise 8.3
Question 1.

Solution:
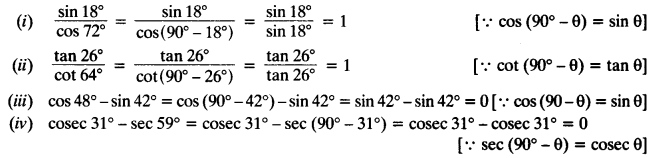
Question 2.
Show that:
(i) tan 48° tan 23° tan 42° tan 67° = 1
(ii) cos 38° cos 52° – sin 38° sin 52° = 0
Solution:
(i) LHS = tan 48° tan 23° tan 42° tan 67°
= tan 48° tan 23° tan (90° – 48°) tan (90° – 23°)
= tan 48° tan 23° cot 48° cot 23° = tan 48° tan 23° .
= 1 = RHS
(ii) LHS = cos 38° cos 52° – sin 38° sin 52°
= cos 38° cos (90° – 38°) – sin 38° sin (90° – 38°)
= cos 38° sin 38°- sin 38° cos 38° = 0 = RHS
Question 3.
If tan 2A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Solution:
tan 2A = cot (A – 18°)
⇒ cot (90° – 2A) = cot (A – 18°) [∵cot (90° – θ) = tan θ]
⇒ 90° – 2A = A – 18° ⇒ 3A = 108° ⇒ A =
∴ ∠ A = 36°
Question 4.
If tan A = cot B, prove that A + B = 90°.
Solution:
tan A = cot B ⇒ tan A = tan (90° – B) [ ∵ tan (90° – θ) = cot θ]
⇒ A = 90° – B ⇒ A + B = 90° Proved
Question 5.
If sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°), where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Solution:
sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°)
⇒ cosec (90° – 4A) = cosec (A – 20°) [cosec (90° – θ) = sec θ]
⇒ 90° – 4A = A – 20° ⇒ 5A = 110°
A =
A = 22°
∴ ∠ A = 22°
Question 6.
If A, Band Care interior angles of a triangle ABC, then show that: sin (
Solution:
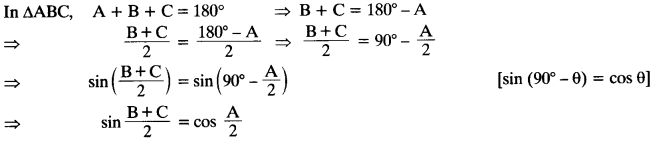
Question 7.
Express sin 61° + cos 75° in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°.
Solution:
sin 67° + cos 75° = sin (90° – 23°) + cos (90° – 15°) = cos 23° + sin 15°
Exercise 8.4
Question 1.
Express the trigonometric ratios sin A, sec A and tan A in terms of cot A.
Solution:
From trigonometric identity, cosec² A – cot² A = 1, we get
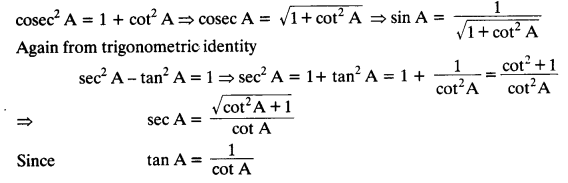
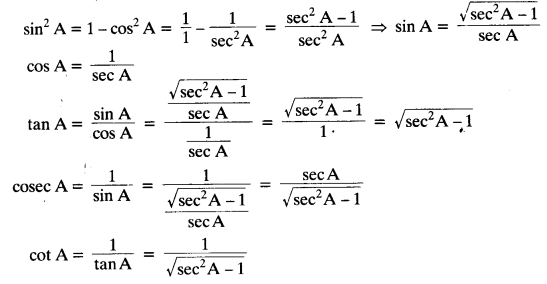
Question 2.
Write all the other trigonometric ratios of ∠A in terms of sec A.
Solution:
Since sin² A + cos² A = 1, therefore
Question 3.
Evaluate:
(i)
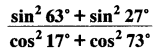
(ii) sin 25° cos 65° + cos 25° sin 65°
Solution:
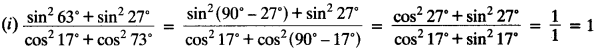
(ii) sin 25° cos 65° + cos 25° sin 65° = sin 25° cos (90° – 25°) + cos 25° sin (90° – 25°)
= sin 25° sin 25° + cos 25° cos 25°
= sin² 25° + cos² 25° = 1
Question 4.
Choose the correct option. Justify your choice.
(i) 9 sec² A – 9 tan² A =
(A) 1
(B) 9
(C) 8
(D) 0
(ii) (1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ ) =
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) -1
(iii) (sec A + tan A) (1 – sin A) =
(A) sec A
(B) sin A
(C) cosec A
(D) cos A
(iv)
(A) sec² A
(B) -1
(C) cot² A
(D) tan² A
Solution:
(i) 9 sec² A – 9 tan² A = 9(sec² A – tan² A) = 9 x 1 = 9
Correct option is (B)
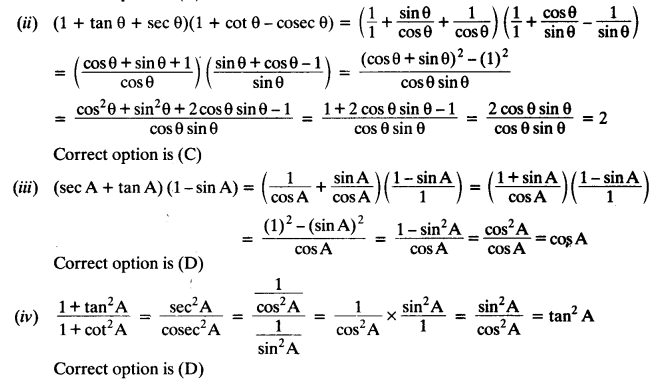
Question 5.
Prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined.
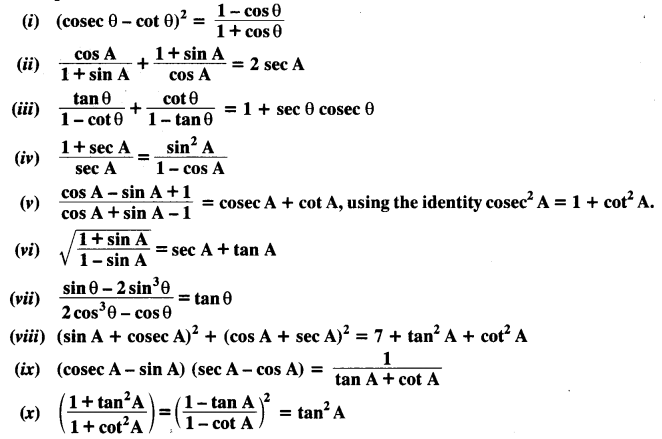
Solution: